The Coxsackievirus in adults is a difficult-to-destroy infection with specific symptoms and treatments. Once in the human body, the virus begins to multiply at a rapid pace and infects internal organs, weakens the work of immune cells. What kind of virus is it, how does it spread, how to treat it dangerous disease? Is it possible to carry out prevention to protect against it?
Enteroviral infection manifests itself in case of poor hygiene and in case of weakened immunity. All viruses do not differ much in symptoms, but are subdivided even in groups. Coxsackie infection has about thirty varieties. From the experience of observing the course of the disease, successfully curing and recovering, it becomes obvious that after that a person develops resistance to the Coxsackie virus. The disease is of moderate severity, and for a reliable diagnosis, it is imperative to contact medical institutions.
In adult patients, infection occurs quite often and almost does not differ from the course of the disease in children. The disease is characterized by the risk of developing myocarditis. In the fight against the disease, strong immunity and the degree of resistance of the body to infections play a role. The male population suffers the most, but the occurrence of the disease in women is not excluded.
Historical information
Mankind has long been faced with infectious infections that differ in characteristic features. This is an outbreak of myalgia at the turn of the 19th and 20th centuries in Spanish cities, an epidemic of serous meningitis in the 20th century in America and France. But in those days, the Coxsackie virus had not yet been isolated separately. Only in the middle of the 20th century, microorganisms were identified as a separate species. The first patients showed symptoms of poliomyelitis. The virus was first isolated from stool sick people in the city of Coxsackie, as a result of which the microorganisms received the desired name.
- A-virus group infects mucous membranes respiratory tract and the eye, while the patient develops conjunctivitis in an acute form, difficulty breathing develops, a rash appears, while neglected conditions become chronic. As a result of infection with this type of infection, serous meningitis, herpesvirus tonsillitis, rapidly developing hemorrhagic conjunctivitis, and vesicular stomatitis occur.
- B virus group causes acute stages of inflammation in the internal organs, localized in the pancreas, heart, pleural region. Microorganisms of this type are pathogenic, the liver is especially often and extensively affected, as a result of which hepatitis develops.
Symptoms of the development of the disease
In order to preliminarily identify the possibility of infection, the specialist studies the symptoms characteristic of the disease. About 10 days pass from the initial penetration into the human body, sometimes there is a rapid development of the Coxsackie virus within two days. Symptoms in adults and children are:

To more accurately determine whether there is a disease in the body, they carry out necessary tests. This allows to identify the virological characteristics and confirm the infection. Sometimes parents begin to suspect something is wrong only after the child has problems with nails, they exfoliate and peel off. But this is a late manifestation of the disease, which refers to neglected conditions. Basically, the disease has a favorable outcome, but sometimes severe complications develop.
How the virus spreads
 The most accessible are the organisms of children preschool age and schoolchildren. Infants are almost not susceptible to infection, since maternal antibodies are present in their body, for babies up to six months it is very important breast-feeding. But it is not possible to obtain complete information about such immunity, since in some cases infants have serious disease obtained as a result of infection with the Coxsackie virus. There are two main ways of penetration of microorganisms into the human body:
The most accessible are the organisms of children preschool age and schoolchildren. Infants are almost not susceptible to infection, since maternal antibodies are present in their body, for babies up to six months it is very important breast-feeding. But it is not possible to obtain complete information about such immunity, since in some cases infants have serious disease obtained as a result of infection with the Coxsackie virus. There are two main ways of penetration of microorganisms into the human body:
- the virus is spreading by drip and through the air, so you can get infected from a virus carrier or an already sick person;
- alimentary way infection involves the transmission of the virus in an unsanitary environment, for example, through dirty hands, sharing utensils with a carrier, unwashed vegetables.
The pathogenesis of infection in the human body

Estimated Forecast
Depending on the development of protective forces human body and at the time of the started treatment, there are several options for further events:
- full recovery occurs;
- disease progresses to chronic stage when microorganisms persist in the internal organs and systems of the body indefinitely;
- a person becomes a carrier of the virus.
Varieties of diseases from the Coxsackie virus
Diseases develop each according to its own scenario and require appropriate treatment:
- flu-like form It is so named because the symptoms are similar to those of the flu and are characterized by high fever. Infection develops within 3-5 days. In the early days, the thermometer readings can rise to 40ºС, but if we talk about the general prognosis of infection, then the disease belongs to the mildest forms and disappears without a trace in a short period of time.
- Enteroviral exanthema manifests itself as a rash on the chest, arms, sometimes on the scalp. The rash gradually becomes blistered, the formations burst, dry crusts appear in their place, peeling and exfoliation of the upper epithelial layer. Often the disease is confused with chickenpox or rubella. The prognosis of the disease is favorable, a short course does not allow the development of various complications.
 If speak about hemorrhagic conjunctivitis, then the disease has a rapid development and affects the eyes within two days. Symptoms of the disease are pain in the eyes, a feeling of sand under the eyelids, a fear of light develops, the release of tears, and sometimes pus. Traces of numerous hemorrhages appear on the proteins, the eyelids are edematous. Characterized by a consistent lesion of one, then the other eye. The general health of the patient remains normal. The disease disappears without a trace within a couple of weeks.
If speak about hemorrhagic conjunctivitis, then the disease has a rapid development and affects the eyes within two days. Symptoms of the disease are pain in the eyes, a feeling of sand under the eyelids, a fear of light develops, the release of tears, and sometimes pus. Traces of numerous hemorrhages appear on the proteins, the eyelids are edematous. Characterized by a consistent lesion of one, then the other eye. The general health of the patient remains normal. The disease disappears without a trace within a couple of weeks.- Herpes sore throat develops in time up to two weeks, and the virus is localized in the mucous layer of the pharynx. Symptoms manifest themselves in the form of high temperatures, general weakness, acute sore throat, headache. A runny nose may join and lymph nodes may enlarge. It is distinguished from the standard sore throat by the appearance of watery bubbles on the surface of the larynx and mouth, which unite and burst over time. The disease in symptoms resembles both stomatitis and tonsillitis.
- penetrates into the liver cells, the disease causes its increase in size and the manifestation of a feeling of heaviness and fullness in the right side. The disease can turn into viral hepatitis and take a chronic form.
- Microorganisms actively penetrate the digestive organs, for example, the intestines. Symptoms appear as pain in the abdomen, peritoneum, frequent dark-colored diarrhea, fever. At the same time, the virus can be localized in the throat or nasal cavity, which causes a malfunction of these organs. Diarrhea lasts up to three days, the body completely defeats the infection within two weeks.
- Form of the disease with symptoms poliomyelitis passes with the characteristic symptoms of this disease, but differs rapid development and not such a deep degree of damage, at the same time a rash on the body, fever, diarrhea joins.
 Cardiac dysfunction occurs when viral myocarditis, endocarditis, pericarditis. At the same time, there is general weakness, pain in the sternum. It leads to severe damage to organs, while the pressure is lowered, high temperature indicators, drowsiness during the day are noted. With damage to the central nervous system, convulsions appear. If no action is taken, the patient may die within a short time.
Cardiac dysfunction occurs when viral myocarditis, endocarditis, pericarditis. At the same time, there is general weakness, pain in the sternum. It leads to severe damage to organs, while the pressure is lowered, high temperature indicators, drowsiness during the day are noted. With damage to the central nervous system, convulsions appear. If no action is taken, the patient may die within a short time.- Development pleurodynia takes place in the form of a change in the work of muscle tissue, the development of myositis. Soreness is observed in all areas of the body, most often in the intercostal region. It is manifested by difficulty breathing, but damage to the pleura is not typical. The pains are aggravated by movement and are in the nature of influxes. Body temperature rises to high limits. The disease in this form is manifested infrequently.
- Viral serous meningitis caused by various types of agents, the Coxsackie virus is one of them. The disease causes damage to the meninges and is manifested by symptoms with an acute onset. The temperature rises to high levels, there is pain in the muscles throughout the body and convulsions. Lack of appetite, pain in the peritoneum and diarrhea join the general weakness, sometimes the disease affects the nasopharynx. In a severe degree of the disease, persistent drowsiness, fainting, paresis and paralysis are observed.
Treatment of Coxsackie virus
Weak forms of infection are treated according to the SARS method in home conditions. For treatment, symptomatic and pathogenetic therapy is used, depending on the severity of the course and the site of introduction of the viral agent.
With a significant increase in temperature use drugs with antipyretic action, for example, Ibufen, Paracetamol, Aspirin, Ibuprofen. Sometimes it is worth taking care of increasing immunity; for this, immunoglobulins and interferons are used.
 With increased intoxication organisms use adsorbents, for example, Enterosgel and activated carbon. As a result of infection and diarrhea, dehydration of the body occurs, therefore, drinking plenty of water is given as an additional treatment. For the treatment of rashes and wounds on the surface of the pharynx and in the mouth, Geksoral and Oracept are used.
With increased intoxication organisms use adsorbents, for example, Enterosgel and activated carbon. As a result of infection and diarrhea, dehydration of the body occurs, therefore, drinking plenty of water is given as an additional treatment. For the treatment of rashes and wounds on the surface of the pharynx and in the mouth, Geksoral and Oracept are used.
Itching on the body treatable with antihistamines. The drugs are prescribed to reduce the scratching of the skin surface by the child, as a result of which infection with bacteria on the surface can join. In severe cases of the disease as a result of Coxsackie infection, treatment with antibiotics and antiviral drugs is added.
In modern pharmaceuticals, there is no universal drug for the destruction of the Coxsackie virus. Medicines, prescribed by a doctor, support the body, help cope with infection and increase immune defenses. For a standard disease in a non-severe form, therapeutic and other measures are indicated.
As additional measures for treatment, gargling of the throat and nose with Mirastamin, Geroksal, treatment in bed is considered. A balanced diet is shown for the entire period, in which proteins, carbohydrates and fiber are present in sufficient quantities, in addition, the necessary vitamins, minerals and trace elements are contained.
Prevention of infection with the Coxsackie virus
Dr. Komarovsky in his speeches advises to keep the body in hygienic clean conditions as a preventive measure. This is characteristic of the distraction of the B virus, but group A microorganisms are spread, for the most part, by droplet and airborne. In this case, hygiene is not topical remedy prevention.
To protect against infection in public places, one should be less likely to be in the crowd during the epidemiological period and abandon joint events, children's entertainment gatherings, matinees, concerts, etc. Hardening is of no small importance, good food and doing sports.
Attention, only TODAY!
Enterovirus infection is a serious threat to the life and health of a child, so every adult should know how to treat the coxsackie virus. The disease is characterized by a polymorphic clinical picture and is a highly contagious disease. Microorganisms that cause the development of the disease prefer the acidic environment of the stomach. However, the infection can be found not only in the gastrointestinal tract (gastrointestinal tract), but also on any organs and tissues in the human body. Cases have been recorded when the coxsackie virus even affected nerve cells.
What is coxsackie virus
Coxsackie virus (coxsackie virus) belongs to the family of enteroviruses, which means that the infection belongs to the intestinal gastrointestinal tract. The first mentions of this disease were discovered in 1950 in the town of Coxsackie (USA). The disease has two varieties: some patients suffer from the a-type virus, others from the b-type. The groups differ from each other in antigenic properties, both representatives of the infection are sensitive to the effects of disinfectant solutions and sunlight. They die in boiling water after 20 minutes.
In all other cases, the above-mentioned virus serotypes show resistance to environmental conditions. Children between the ages of 3 and 10 are most at risk of infection. One of the main features of the disease is the lack of formation of stable immunity after the transfer of the disease. The coxsackie virus is sometimes called the "summer flu" due to the occurrence of the epidemic period mainly in the warm season. The disease is the cause of the hand-foot-mouth syndrome, which includes manifestations of enanthema and exanthema.
Incubation period
The first signs of intestinal flu are similar to the symptoms of a cold: deterioration of health, severe fever, inflammation of the muscles thoracic. The incubation period of the disease lasts from 2 to 10 days, after which the negative manifestations become more noticeable. On the feet, palms, forearms, genitals, or even in the mouth of patients, bubbles with liquid appear, which are similar to an allergic reaction.
These neoplasms do not cause severe itching, but cause pain upon contact. The virus affects the condition of the intestines and stomach, which leads to vomiting or diarrhea. In the absence of proper treatment, the infection can cause the following complications: viral meningitis, diabetes, myocarditis, paralysis, inflammation of the central nervous system (central nervous system).
General symptoms of the disease
Specific symptoms that indicate the development of this disease begin to develop about a day after infection. Characteristic signs of the presence of an enterovirus infection in the human body are the appearance of painful small vesicles or ulcers on the oral mucosa. Such growths can cover the tonsils, causing sore throats.
The appearance of vesicles on the palms and feet indicates the progression of the coxsackie virus, outwardly the rash resembles chickenpox. Also, patients have a high temperature, which persists for several days. In the classical course of infection, the condition returns to normal after a couple of days. Against the background of the above manifestations, dyspeptic syndrome develops, which involves diarrhea and vomiting.
Treatment of the coxsackie virus
The disease is treated symptomatically or supportively, since the vaccine against the coxsackie virus has not yet been invented. At the moment there are no specific medications against this infection, but complex treatment ailment the doctor will be able to pick up effective drugs. It is important to remember to follow the rules of personal hygiene, since one of the ways the virus is transmitted is fecal-oral (dirty hands disease).
If you have symptoms of dehydration, you should definitely drink the norm of water per day to prevent further development of intoxication. Local anesthetics are prescribed for the treatment of an inflamed red throat or sores in the mouth. Fukortsin and Zelenka are used in the treatment of a rash on the patient's skin. For headaches and fever, experts recommend taking all kinds of anti-inflammatory drugs, for example, Ibuprofen. In the case of a severe infection, it is necessary to use antiviral drugs, such as Amiksin.
In adults
Any adult with a weakened immune system can pick up a childhood infection. In order to get sick, contact with a carrier of the coxsackie virus is enough. Infection by airborne droplets is one of the most common ways of transmission of enterovirus fever, which has been confirmed by numerous clinical cases. Sometimes it is problematic to make a correct diagnosis for a patient, because some types of the virus are characterized by asymptomatic development.
Treatment for coxsackievirus in adults depends on the severity of the symptoms. When diagnosing a disease, strong antiviral drugs should be taken during the first three days. Further progression of the infection indicates the need for the appointment of symptomatic therapy, which includes: diet, bed rest, intake of large amounts of fluid.
In children
If a child shows signs of an infection, stop visiting public places and call the local pediatrician. Treatment of the coxsackie virus in children follows the same pattern as in adults: antipyretics or antihistamines, solutions, throat sprays are prescribed. An integrated approach to therapy will provide all the necessary conditions for the patient's body to self-recover, which occurs approximately 10-12 days after infection.
Parents should give their baby plenty of warm fluids to reduce fever and flush out toxins as quickly as possible. The disease rarely causes complications, but in advanced cases, the infection can cause serious damage to the health of the child. This occurs when the virus spreads through the systemic bloodstream, which creates fertile ground for the penetration of microorganisms into the internal organs. Cases of development of serous meningitis, paralysis, necrosis of muscle tissues, lesions of the meninges and other serious consequences have been recorded.
This implies the use medicines to reduce fever, anesthetize rashes or treat wounds on the skin. For successful treatment, the patient should adhere to a proper diet, drink plenty of water and rest. Strengthen the immune system with the help of medicines such as vitamins, interferons, sorbents, antibiotics, antiseptics.

Topical remedies to reduce itching
During the course of the disease, the patient has a large number of negative symptoms, one of which is severe itching. Small child unable to endure the discomfort caused by the condition for long, so doctors often prescribe antihistamines for relief local action. These include Fenistil or Vitaon baby gel, Zirtek or Suprastin are best suited for adults. The above remedies help to quickly eliminate itching and normalize the patient's well-being.
Antipyretic drugs
This category of drugs is used for the first few days in the treatment of the coxsackie virus, until the person's immunity produces lymphocytes and other protective cells to eliminate the infection. At acute stage During the course of the disease, the patient's temperature can rise strongly (up to 39-40 C), so the use of antipyretics is an important part of the treatment. Experts recommend using Paracetamol and Nurofen for both children and adults. These drugs are considered safe for human health if the specified dosage is observed.
Reception of enterosorbents
To speed up the process of removing toxins from the body, it is necessary to observe the drinking regimen and take enterosorbents. The coxsackie virus often leads to intoxication, therefore, to alleviate negative symptoms, patients take Polysorb, Enterosgel or Laktofiltrum. The above funds absorb harmful microorganisms that have settled in the gastrointestinal tract, which helps to eliminate the infection in a short period of time.
Antiviral drugs for the treatment of coxsackievirus
In severe cases of the disease, when it is difficult for the body to cope with the infection on its own, doctors recommend the use of antiviral drugs. by the most effective tool for immunocompromised children is Gamma globulin, which is developed on the basis of donated blood. It is often used for prevention during an outbreak of the coxsackie virus or if the child has been in contact with an infected person. Amiksin is indicated in rare cases in the treatment of adult patients.
Antiseptics for the treatment of the oral cavity
The Coxsackie virus affects not only the skin, but also the mucous membranes in the human body. Severe sore throat, sores, or rash in oral cavity cause the patient severe discomfort, so doctors prescribe symptomatic treatment. For rinsing the mouth, special antiseptics and anti-inflammatory drugs are used, which effectively remove pain. Children are prescribed a decoction of chamomile or a soda solution, adults use Geksoral, Miramistin, Stomatidin.

Antihistamines
Medicines from this category are used to alleviate negative symptoms with general intoxication of the body. Patients suffering from enteroviral eczema use antihistamines to relieve the discomfort of the disease. To eliminate itching, doctors prescribe the following medications: Erius, Claritin, Telfast, Psilo-balm. Listed medicinal substances Suitable for both outdoor and internal use, based on the form of release of the drug.
Vitamins and trace elements
The Coxsackie virus can cause serious damage to an organism with a weak immune system. For this reason, experts recommend taking B and C vitamins not only during therapy, but also during an outbreak. In order to protect yourself from an enterovirus disease, it is important to provide a supply of trace elements necessary to maintain the body's defense mechanisms. Vitamins help fight the manifestations of intoxication and stimulate the elimination of toxins, which favorably affects the patient's condition.
How to treat coxsackie virus during pregnancy
In most cases, enterovirus diseases during pregnancy do not pose a threat to the health of the mother or fetus. Manifestations of the coxsackie virus resemble a cold, so symptomatic treatment of pregnant women is an effective remedy against infection. However, it is very important to recognize the disease in time in order to prevent the development of complications. For these purposes, they resort to laboratory diagnostics, because it is impossible to accurately identify the disease from a photo from the Internet. After identifying the problem, the patient must go through several stages of treatment:
- Admission to a local hospital for professional medical care.
- The appointment of detoxification therapy, which allows to eliminate the symptoms of the coxsackie virus.
- Bed rest, drinking plenty of water.
- Collection of blood, urine, stool tests to determine the type of infection.
- Regular monitoring of the fetus with ultrasound.
Enterovirus prevention
There is currently no specific vaccine against the coxsackie virus, which is directly related to the variability of the infection. In order to protect yourself and your family from enterovirus disease, doctors recommend following the basic rules of hygiene. For example, Dr. Komarovsky is convinced that it is important to lead healthy lifestyle life, eat right and alternate physical activity with rest.
What it is? Coxsackievirus is a group of 30 active enteroviruses that replicate in gastrointestinal tract child. Epidemic caused by virus spreads as intestinal diseases among children younger age. The disease was first diagnosed in the small US town of Coxsackie, and due to the high level of contagion, it quickly spread around the globe.
These viruses are considered "children's", since children from 3 to 10 years old get sick mainly. An outbreak of the Coxsackie virus is characterized by the defeat of a significant number of persons in close contact, with a wave-like course of clinical symptoms lasting up to 21 days. In the article, we will consider: what kind of virus it is, the causes and symptoms of the disease, what treatment is effective for the Coxsackie virus, as well as the main methods of prevention in children.
What is the Coxsackie virus?
Coxsackievirus is a viral infection belonging to the family of herpetic viruses that live and multiply in digestive tract person. Coxsackie is often manifested by the hand-foot-mouth syndrome. The syndrome gets its name from the typical rashes that cover these parts of the body. Its symptoms resemble the well-known stomatitis, intestinal flu, sometimes the disease is misdiagnosed as acute poliomyelitis.
98% contagious - if we are talking about close contact with the patient or his things.
The main risk category for the development of a disease caused by the Coxsackie virus or the development of a virus carrier are children from 3 to 10 years old, while in newborns, as well as breastfed infants, persistent immune defense mechanisms are formed in the body that prevent the development of the disease.
In adolescents and the adult population, the Coxsackie virus, after entering the body, does not provoke the development of active clinical symptoms and has a latent course with the subsequent formation of immunity.
Ways of transmission and main causes of the disease

Coxsackie is a disease of dirty hands. 97% of infections occur through food - through hands, dishes, unwashed fruits, tap water. That is why the virus mainly affects young children who have not yet developed strong hygiene skills (wash hands, do not drink raw untreated water). The category most susceptible to the disease is children of preschool and primary school age.
A person can become infected from another sick person, and often from a virus carrier. Often people pick up an infection in hotels in Turkey, Cyprus or other places of recreation.
In the first few days of the disease, the Coxsackie virus is maximally concentrated in the nasopharyngeal mucus, while its active reproduction occurs in the human intestinal lumen, which creates conditions for the transmission of the virus by the fecal-oral route. Direct infection of the macroorganism occurs at the time of consumption of contaminated food and water.
The time between the introduction of the virus and its activation is called the incubation period. For the Coxsackie virus, it is from 2 to 10 days. After the incubation period comes acute form illness. Visible symptoms appear - fever, indigestion, rash on the palms and feet, rashes inside the mouth.
How can you get infected?

You can get the virus through drinking water and water in swimming pools, as well as through contaminated food. Enteroviruses spread rapidly if personal hygiene rules are not followed. It is enough for the patient to visit the toilet, not wash his hands and use household items to spread the infection throughout the house.
You can protect the child from infection and carry out prevention initially. Therefore, doctors strongly recommend that all parents give their children to drink only purchased filtered water, and wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly before use. This will be the prevention of infection with the Coxsackie virus.
Important! The patient should be isolated from healthy children and adults. It is desirable that the isolation lasts about 1-1.5 weeks.
The outcome of the infection is determined by the type of virus and the personal characteristics of the patient's body:
- The person recovers completely (all viral particles are destroyed).
- The process becomes chronic (neurons and internal organs retain the virus indefinitely).
- The patient becomes a virus carrier.
How is the infection progressing?

The main features of entero viral infections:
- almost always - this is an acute onset;
- the infection usually proceeds violently, the patient is put to bed;
- manifestations of enteroviruses can be very diverse;
- relatively quickly recovery occurs;
- complications rarely develop;
- The most dangerous is the Coxsackievirus group B.
Measures of specific prevention (vaccination) against the Coxsackie virus have not been developed to date.
In addition to these types of diseases, they share the forms and variants of the course of enterovirus diseases.
Coxsackie viruses are divided into two large groups:
- type A virus (causes meningitis and infectious diseases throat);
- type B virus (causes inflammatory and degenerative changes in the brain, muscles and heart).
Course options: light, medium and heavy.
The severity of the course of the disease primarily depends on the degree of damage to vital organs (the brain and its membranes, heart, liver), as well as the severity of intoxication.
In addition, the course of enteroviral infections can be:
- smooth - recovery occurs within 10-20 days;
- wavy;
- recurrent;
- with complications.
Forms of the disease:
- isolated - in the presence of only one syndrome;
- combined - when the virus affects several organs and systems.
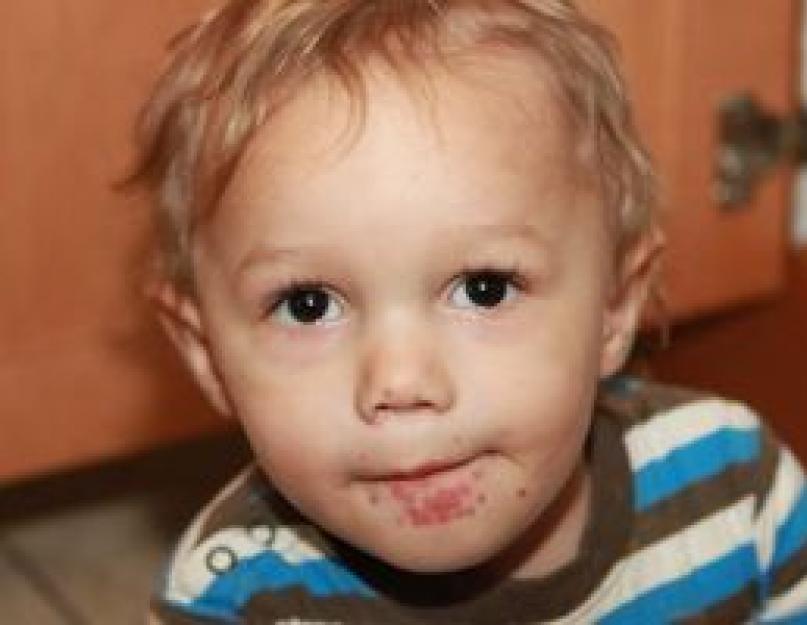
Symptoms of the Coxsackie virus and photo
The incubation period from the moment of infection, before the first signs in the form of rashes appear, is about 10 days. Other symptoms also appear, such as:
- A sharp increase in body temperature up to 38 degrees and above;
- taxation of the tongue;
- general weakness;
- sore throat;
- malnutrition;
- cervical enlargement lymph nodes.
In the photo below, the characteristic signs of the Coxsackie virus:


Depending on the prevalence of any symptom, there are several clinical forms of this disease:
- Herpangina or enteroviral vesicular. This is an infection that provokes the development of sores on the tonsils and soft palate and back of the throat.
- epidemic myalgia- the leading symptom is the development of pain in all muscle groups.
- Pathology of the nervous system- damage to the membranes of the brain (serous meningitis). A more severe form of infection with the development of severe headache, severe intoxication. Some serotypes of the Coxsackie virus can lead to the development of temporary paralysis of the muscles of the legs (remind).
- Enteroviral fever- characterized by the absence of specific symptoms, there is only a rise in body temperature and poor general well-being of the child.
- Enteroviral exanthema- The main manifestation of infection is the appearance of a rash on the skin.
Complete healing of red blisters is observed after 6-7 days, and the rash - after 10-12. The occurrence of complications depends on the quality of treatment and the timeliness of contacting a doctor. How to treat the Coxsackie virus is better to ask the doctor. Doctors advise to relieve fever and pain with Paracetamol or Ibuprofen.
Coxsackie virus in children
The disease can easily be confused with chickenpox or allergies. The virus has several symptoms and can also occur in various countries. Incubation period, or the time from infection to the first symptoms of the disease, with the Coxsackie virus is usually 3-6 days, less often from 2 to 10 days. A child already in this period may have a poor appetite, become lethargic and drowsy, act up.

Symptoms of the Coxsackie virus in children:
- fever;
- headaches of varying degrees of intensity;
- severe weakness;
- chills;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- catarrhal phenomena - runny nose, pain or perspiration in the oropharynx;
- loss of appetite;
- muscle pain (myalgia);
- fast fatiguability;
- heartbeat;
- in the younger age group - false croup.
Very often, the Coxsackie virus is confused with a rash with allergies (including antibiotics), or chickenpox, since the clinical manifestations of these diseases are similar.
The Coxsackie virus in children in the photo with herpangina looks like a specific plaque on the arches of the palatine tonsils, tongue, back of the pharynx.
The disease caused by the Coxsackie virus in children can occur in two forms:
- typical;
- atypical.
Typical forms of the disease manifest themselves in the form of lesions:
- isolated (enteroviral tonsillitis, exanthema or fever, hepatitis, myalgia and gastroenteritis);
- nervous system (serous meningitis, encephalitis, paralysis and encephalomyocarditis of newborns);
- heart (endocarditis, pericarditis and myocarditis);
- genitourinary system (orchitis, epididymitis, cystitis);
- eyes (uveitis - inflammation of the choroid, conjunctivitis).

Due to the fact that the initial signs have a lot of similarities with SARS, the diagnosis sometimes ends in this process, and then the wrong decisions on treatment are made. This exacerbates the overall picture. But after 1-2 days, other phenomena appear on the palms and feet - a rash in adults and children (vesicles are 3 mm in diameter).
Hand-foot-mouth syndrome is also often observed - a rash appears simultaneously on the oral mucosa, palms and feet.
An urgent call to a pediatrician is necessary if a child has:
- Paleness of the skin;
- The appearance of blue on the body, near the ears, between the fingers;
- The occurrence of signs of dehydration: lethargy, dry lips, decreased urination, increased sleepiness, delirium, dizziness;
- Sharp headache;
- Refusal to eat;
- Long fever.
With severe infection, urgent hospitalization is necessary.
Treatment for children includes:
- bed rest for the entire period of intoxication,
- a diet with enough fluids and vitamins,
- plentiful drink,
- in case of severe diarrhea and vomiting - taking rehydration solutions.
Sick children are quarantined for 2 weeks. The prognosis of treatment in most cases is favorable. After the disease, persistent specific immunity develops.
The doctor may need to re-check for the presence of Coxsackie viruses in the body. This rarely occurs, but sometimes in children the disease becomes additionally inflamed. Signs of a contagious infection are dehydration in which the child refuses to swallow because of a sore throat. If the newborn refuses food or water, moisten the nipples more than usual and call the doctor.
For prevention, special attention should be paid to:
- Drinking water (as well as in the pool, where the child can take a sip while swimming);
- Food (strong heat does not contribute to long-term storage of food);
- Protect children from sun and heat stroke.
Coxsackie virus in adults
Coxsackievirus in adults is a rare medical case. The older the person, the less likely he is to contract such an infection. The routes of entry of the virus are the same for patients of any age.
If infection with the Coxsackie type A virus has occurred, and everything is in order with the immune system, the infection is often asymptomatic. Sometimes the following symptoms are observed:
- redness of some skin areas;
- small papular rash of pinkish color;
- brief fever.
With the type B virus in adults, the following symptoms are possible:
- the appearance of redness, rash;
- loss of appetite;
- heat;
- sore throat;
- cough;
- runny nose;
- diarrhea.
For general health In an adult, the disease does not carry any dangerous phenomena and consequences. A rash on the body with a competent approach will pass quickly, leaving no consequences for the general internal state of health.
Possible Complications
The Coxsackie virus usually passes quickly and leaves no consequences. But in rare cases, complications develop:
- dehydration of the body;
- pulmonary edema;
- Iron-deficiency anemia;
- diabetes;
- severe forms and myocarditis.
Diagnostics
Which doctor should I contact when the first symptoms appear? If a person has or suspects the development of the Coxsackie virus, a person should immediately seek help from such doctors as an infectious disease specialist, an epidemiologist.
Enterovirus infection is diagnosed on the basis of:
- examination of the child;
- a blood test for the detection of pathogen RNA and antibodies to it;
- analysis of feces, flushing from the nasal mucosa, scrapings from the skin or conjunctiva (depending on the location of the lesion).
How to treat the Coxsackie virus

If the disease proceeds without complications, then it is treated in the same way as conventional ARVI. Basically, it is enough to be treated at home. Pathogenetic and symptomatic therapy is carried out:
- If the child has a high fever, then antipyretics should be taken: Ibuprofen, Paracetamol, Ibufen.
- To increase immunity, the use of immunomodulators is indicated: interferons or immunoglobulins.
- Antipyretics - give with poor temperature tolerance (ibuprofen, paracetamol). With normal tolerance, the temperature is not brought down (a rise in temperature is a protective reaction of the body, which helps to control and limit the reproduction of the virus).
- Antiseptics: soda and salt rinses are used to treat the mouth, and fukortsin and greenery are used to treat the skin. To reduce itching - baths with soda. They can also prescribe: Tantum Verde, Geksoral.
- Antihistamines, topical or general action to reduce itching - Vitaon Baby, Fenistil gel, Suprastin, Zirtek.
- Antibiotics: application antibacterial drugs with the Coxsackie virus is allowed only when a bacterial component is attached with the preferred use of agents with a wide range antimicrobial activity.
- To support the immune system, it is necessary to ensure an adequate supply of vitamins and trace elements, which are sold in pharmacies as over-the-counter supplements. Echinacea, shiitake mushrooms and goji berries also have a positive effect on the immune system.
Treatment skin rashes also not carried out. It is recommended to protect the elements of the rash from scratching, and also not to take a bath until complete recovery. Local therapy with skin forms of the disease is not prescribed.
If a child or an adult is dehydrated, it is worth paying attention to taking the amount of water that the body needs to maintain normal life.
Food
- Feed in small portions, but often (5-6 times a day).
- Avoid salty, spicy and sour foods.
- Prepare food by steaming, baking or boiling.
- Include foods rich in vitamins (fruits, vegetables) in your diet.
You can treat the disease with folk remedies:
- Rinse your mouth with a decoction of chamomile.
- Drink tea with cinnamon and honey. It soothes a sore throat.
- Eat more garlic, which resists viral infection.
Prevention of the Coxsackie virus in children and adults
Prevention of the Coxsackie virus will help to avoid the disease:
- Wash your hands with soap and water after walking and going to the toilet.
- Use only purified drinking water.
- Food must be treated with boiling water.
- Do not use common cutlery: let each family member have their own cup, spoon, fork.
If someone in the family is still infected with the Coxsackie virus, be sure to provide him with separate personal hygiene items, which will reduce the chance of transmitting the infection to healthy people. Do not forget about the thorough maintenance of cleanliness in the house. Personal hygiene products such as pads, diapers, wipes, etc. must be disposed of immediately after use.
Prevention of any disease depends on the degree of protective mechanisms. It is necessary to harden the child, to be in the fresh air more often and to eat right so that the immune system is normal.
This is all about the Coxsackie virus in children and adults: what are the causes of the disease, symptoms and treatment features. Be healthy!
The sensational Coxsackie virus in Turkey in 2017 frightened many tourists who ordered summer holidays. Although for several years now there have been warnings about the danger of getting sick in Turkish resorts, only this year the disease has taken on serious proportions.
At the moment, Rospotrebnadzor still recognized some resort towns in Turkey as dangerous in terms of medical problems, although the Turkish Ministry of Health still calls all incoming information speculation.
In any case, no one wants to lie with a high temperature and be isolated from entertainment instead of a carefree vacation on the beach. In addition, rested tourists bring the disease to Russia, Ukraine and other countries. Therefore, everyone should know how the Coxsackie virus manifests itself, how dangerous it is and what actions to take if a disease is suspected.
What is the Coxsackie virus, how is it transmitted?
The Coxsackie virus is a group of enteroviruses (about 30 serotypes) that enters the human body through the oral mucosa and rapidly multiplies in the intestine. The virus is often called "Turkish chickenpox", but the disease has characteristic differences and sometimes proceeds in a severe form with damage to the brain, heart, liver.
The virus is quite stable in the external environment, pathogenic microorganisms feel great in the aquatic environment (drinking water, swimming pools), on fruits and die only when boiled or exposed to high temperatures. You can become infected with the virus by airborne droplets, contact (toys in kindergarten, dirty hands, swimming in the pool and the sea) and food (with dairy products, unwashed fruits, water).
Most often, children 4-10 years old get sick, but infection of adults is not excluded. The infection is not dangerous for babies under 3 months old, they are protected from the disease by antibodies obtained with mother's milk. In this case, the disease can proceed quite easily and be diagnosed as acute respiratory infections, or lead to serious consequences and require hospitalization of the patient.
The incubation period for the Coxsackie virus is 2-7 days. The patient is contagious to others from the first day of the onset of painful symptoms and remains dangerous in terms of infecting other people until complete recovery.
After the disease, persistent immunity is formed, but only to a certain serotype of the virus. Therefore, there is every chance of getting sick again with the Coxsackie virus of a different serotype.
Common symptoms of the Coxsackie virus

The Coxsackie virus causes symptoms characteristic of enterovirus infections. The classic picture of the course of the disease is as follows:
- The onset of the disease: intoxication
Suddenly, the infected person's temperature rises to 39-40ºС. Adults note headache, weakness and drowsiness, aches all over the body. In children, the Coxsackie virus often provokes vomiting and convulsions against the background of high fever. Kids refuse to eat, become whiny, heartbeat quickens. Often, redness appears in the throat, submandibular lymph nodes increase. characteristic feature viral intoxication is a white or yellowish coating on the tongue.
- Eruption Period: Mouth-Hand-Leg Syndrome
After 1-2 days from the onset of hyperthermia, the patient's condition worsens, on the inner surface of the cheeks and lips, on the outside around the mouth, watery bubbles with a diameter of about 2 mm are formed. Their spontaneous opening leads to the formation of ulcers.
Unlike ordinary stomatitis, mouth ulcers with Coxsackie's disease have a bright red bottom.
During this period, abundant salivation is noted, the child completely refuses to eat because of severe pain. Simultaneously with rashes in the mouth, the same bubbles appear on the skin. The palms and feet are dotted with small elements, single elements of the rash can be found on the buttocks, the flexor surface of the forearms (from the wrist to the elbow).
Important! Unlike chickenpox, the skin rash with the Coxsackie virus does not provoke itching and is not spread throughout the body. However, children can scratch watery blisters, which can lead to festering, especially in hot weather.
- convalescence period
After 5 days the immune system begins to produce antibodies, T-lymphocytes rush to the focus of a viral infection: the symptoms of the disease begin to fade, the patient's condition gradually improves. The recovery period lasts 5-7 days, the sores are delayed.
As a rule, immunity completely destroys the virus. However, in rare cases (immunodeficiency, individual characteristics of the body), Coxsackie lingers in the nerve endings, like the herpes virus. At the same time, it forms chronic form disease or virus infection.
Specific symptomatic forms of Coxsackie's disease
Depending on the predominant localization of specific rashes and the severity of symptoms, the Coxsackie virus in a child can proceed with atypical scenarios:
- flu-like form
It usually manifests itself when re-infected with the virus, the easiest variant of the course of the disease. The symptoms of the disease are similar to those of ARVI, so Coxsackie's disease with such symptoms is called "three-day fever", "summer flu". The flu-like form is characterized by hyperthermia for 3 days, rashes on the skin and mucous membranes are single or absent. Recovery begins on the 4th day, there are no serious consequences.
- intestinal form
Coxsackie's disease with severe intestinal syndrome is the most common. The main symptoms of the disease: abdominal pain and diarrhea up to 8 times a day, accompanied by rumbling and swelling, for 3 days. In children, the Coxsackie virus with a predominant dyspeptic syndrome can provoke nausea and vomiting.
At the same time, the stool is watery, in rare cases, mucus and blotches of blood appear. Severe dyspepsia lasts up to 3 days, all symptoms completely disappear after 10-14 days.
Important! In children under 2 years of age, the Coxsackie virus, inhibiting the synthesis of the lactose enzyme, provokes intolerance to dairy products. Children react to milk intake by sudden vomiting.
- Herpangina
Characteristic symptoms usually appear after 1-2 weeks. after infection with the Coxsackie virus. On the tonsils and mucosa of the upper palate (there are more rash elements around the uvula than on the tonsils), watery vesicles first appear (this distinguishes a viral infection from a classic sore throat), and then small white sores form. Symptoms of the disease, provided that the bacterial flora is not infected, disappear after 1 week.
- Hemorrhagic conjunctivitis
It develops after 2 days from contact with the infection. Painful symptoms first appear in one eye, and then in the other. The feeling of sand in the eyes is accompanied by photophobia and profuse flow of tears, pain when blinking.
On the inner surface of the edematous eyelids, multiple hemorrhages can be found - red dots. Pus is often released from the eyes, but the symptoms of viral intoxication (high temperature, weakness, etc.) are mild. Full recovery occurs after 2 weeks.
- Enteroviral exanthema ("Boston fever")
Has a generalized distribution skin rash. Watery vesicles extend to all arms, shoulders, chest, may be found on the head. Bursting bubbles are quickly tightened with a crust. There are usually no complications, with the exception of suppuration of the combed elements. After healing, the exanthema often peels off and peels off the skin, the nails come off.
Important! The Coxsackie virus, manifested by exanthema, is most similar to chickenpox. However, the bubbles pass much faster - for 3-5 days.
Severe forms of the disease
Spreading with blood, the Coxsackie virus can affect vital organs. In this case, the disease is extremely difficult, often there is a threat to life.
- Serous meningitis
The Coxsackie virus in Turkey in 2017 often occurs precisely with damage to the meninges. Wherein incubation period can be reduced to 1-2 days. Viral meningitis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Sudden onset with high fever, severe headache and severe weakness, up to drowsiness and fainting;
- Stiff neck muscles - the patient cannot tilt his head forward and bring his chin to his chest;
- Photophobia, indomitable vomiting without relief;
- Complete lack of appetite, sore throat, sometimes cough and runny nose;
- Dyspeptic syndrome - diarrhea, spastic abdominal pain, bloating;
- Paresis - a decrease in strength in the limbs, severe muscle weakness.
Symptoms begin to subside after 3-5 days.
- Viral damage to the heart
It is extremely rare - when infected with the Coxsackie group B enterovirus. Most often, this form of the disease is diagnosed in newborns from 3 months. The virus can penetrate into all membranes of the heart, causing pericarditis, endocarditis or myocarditis. Against the background of high temperature, there is pain in the chest, shortness of breath, pressure decreases, the pulse quickens (tachycardia).
The patient is greatly weakened, constantly in a half-asleep state. Often there are edema, arrhythmia, hepatomegaly develops, in severe cases, protracted convulsive seizures are possible. Without emergency resuscitation, death occurs within a few hours from the onset of the disease.
- Poliomyelitis-like form
Against the background of fever, rashes and diarrhea, paralysis rapidly develops. However, the damage to the motor nerves is not as deep as in the disease of the same name, muscle tone is fully restored after recovery.
Important! Unlike Coxsackie's viral infection, paralysis in poliomyelitis develops gradually.
- Viral myositis
An extremely rare form of the disease. The virus, which rapidly multiplies in the muscles, leads to pain in different parts of the body against the background of an increase in body temperature. However, most often the lesion is localized in the intercostal spaces.
The pain intensifies with breathing / coughing, movements (walking, turning the body) at certain intervals, therefore this form of the disease is called the “damn fight”. The name "pleurodynia" does not quite correctly reflect the viral lesion: the pleura is not included in the pathological process.
- Hepatitis
Damage to the liver by the Coxsackie virus in terms of symptoms is fully consistent with hepatitis. Against the background of an enlarged liver, there is an eructation of bile, heaviness in the right side, jaundice.
Photography can be unpleasant

The virus can be passed to the baby at birth
When a pregnant woman is infected in the first trimester, the risk of miscarriage increases by 20%. It is not known for certain whether the Coxsackie virus causes fetal malformations. However, in newborns from mothers who have had some serotypes of the Coxsackie virus, the risk of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus increases dramatically.
The disease can manifest itself not only in the neonatal period, but also at 10-15 years. It is also known for sure that in childbirth a sick mother (there are symptoms of the disease) in 50% of cases transmits the infection to the child.
How to treat the Coxsackie virus in children and adults? Need antibiotics?
The uncomplicated course of Coxsackie's disease - the absence of signs of damage to the meninges, heart and liver - does not require antibiotic therapy. Basically, treatment is reduced to symptomatic therapy:
- You can lower the temperature with the help of Ibuprofen (Ibufen syrup for babies, Mig-400 for adults), Paracetamol (the best option for children, they quickly remove the heat of the candle);
- To prevent dehydration and alleviate the symptoms of intoxication, you should drink plenty of water (boiled!);
- With diarrhea, it is advisable to take Enterosgel, activated carbon(for adults up to 8 tablets per reception), spasmodic pain in the intestines is excellently eliminated by No-shpa;
- Gels used for teething in babies (Kalgel, Dentinox) or Lidocaine solution in ampoules to lubricate lesions (lidocaine contained in gels can cause an allergic reaction and reduce pressure if used too often) helps to facilitate food intake and relieve pain in the mouth. );
- For the speedy healing and prevention of infection of sores in the mouth, Oracept, Ingalipt, Geksoral are used;
- With severe anxiety and itching, the use of antihistamines is justified (the best for babies is Fenistil drops).
When treating the Coxsackie virus, both the severity of the symptoms of the disease and the general condition of the body should be taken into account. Features of the treatment of the disease:
- The Coxsackie virus in adults usually proceeds easily according to the type of SARS.
- Antibiotics do not work on the Coxsackie virus! Taking antibacterial agents is advisable only with suppuration of ulcers (Levomekol ointment, Baktroban), severe disease (for example, meningitis).
- Reception antiviral agents useful only in debilitated people.
- Cold drinks and ice cream can help relieve mouth pain.
- After each meal, rinse your mouth with boiled water at room temperature. An excellent addition would be dilution in a glass of water 1 tsp. soda or salt.
- No one can predict the severity of the disease. Call emergency care essential for severe headaches and tension neck muscles, the appearance of shortness of breath and severe tachycardia, fainting and delirium, as well as critical temperature and rare urination in young children or severe hyperthermia lasting more than 5 days without a tendency to normalize the temperature.
- The introduction of immunoglobulin to patients is not justified. However, for people who are in contact with a sick person or who are in the focus of infection, the introduction of immunoglobulin, although it does not exclude the disease, will help to transfer Coxsackie's disease to mild form and prevent complications.
- The patient is isolated for 1.5-2 weeks until the symptoms of the disease disappear completely.
Virus infection prevention
Although the Coxsackie virus is extremely contagious - upon contact with a sick person, infection occurs with almost 100% probability - preventive actions aimed at preventing the spread of infection. Prevention includes:
- Isolation of the patient for 1-2 weeks. Until the symptoms of the disease disappear completely.
- If you are in foci of infection (for example, in a resort in Turkey), refuse to visit pools, mass events. Such restrictions apply especially to children.
- Double wet cleaning daily in the room where the patient is located, and regular ventilation.
- The introduction of immunoglobulin to young children and pregnant women who were in the focus of infection.
- Boiling water, thoroughly washing fruits and then dousing with boiling water.
- Compliance with the temperature regime and shelf life of dairy products.
- Disinfection of cutlery, toys, boiling underwear and bed linen of the sick person. Separate dishes and towels are allocated for the patient.
- Frequent hand washing, treatment with alcohol-containing antiseptics.
Do not be irresponsible about summer infections, they often lead to serious complications. Most patients infected with the Coxsackie virus do not require hospitalization, have no negative consequences and recover in 10-14 days.
The most severe disease occurs in children under 2 years of age and people with immunodeficiency. Babies are at high risk of dehydration, especially with vomiting and diarrhea. Also important is the timely diagnosis of viral infection and health care during the development of critical conditions. In severe cases of the disease, laboratory confirmation of the presence of the Coxsackie virus is necessary, but not all clinics perform such an analysis.
Thanks
The site provides reference information for informational purposes only. Diagnosis and treatment of diseases should be carried out under the supervision of a specialist. All drugs have contraindications. Expert advice is required!
Which doctor should I contact with the Coxsackie virus?
If the Coxsackie virus provoked an infection of the type of a minor illness (summer flu), when the body temperature rises sharply, the lymph nodes increase, headache, weakness, lethargy, muscle aches appear, loss of appetite, redness of the pharynx and palatine arches, redness of the eyes, then need to contact general practitioner (make an appointment) or pediatrician (make an appointment). If the Coxsackie virus provoked the development of herpangina (the arches, tonsils and uvula are red, there are whitish papules on the palate, tonsils and arches, which after 2-3 days turn into vesicles that burst and leave ulcers, while there is high fever, weakness, body aches , headache and other symptoms of intoxication), you should contact otolaryngologist (make an appointment) or a general practitioner (in the case of children, a pediatrician).
If the Coxsackie virus provoked the development of herpangina (the arches, tonsils and uvula are red, there are whitish papules on the palate, tonsils and arches, which after 2-3 days turn into vesicles that burst and leave ulcers, while there is high fever, weakness, body aches , headache and other symptoms of intoxication), you should contact otolaryngologist (make an appointment) or a general practitioner (in the case of children, a pediatrician).
If the Coxsackie virus provoked an infection of the hand-foot-mouth syndrome type, when the body temperature first rises, and then, against the background of its fall, red viral rashes appear on the skin (such rashes are most often localized around the mouth, on the palms and feet, but can be on the body, under the hair, on the buttocks), it is advisable to refer to infectious disease doctor (make an appointment), but you can go to an appointment with a therapist or pediatrician.
If the Coxsackie virus proceeds according to the type of Bornholm's disease, when a person has paroxysmal very severe pain in the muscles (often there is pain in the intercostal muscles, causing shortness of breath, and pain in the upper abdomen, similar to appendicitis, peritonitis, etc.), which disappear after 3-4 days, you should definitely contact an infectious disease specialist. This is due to the fact that after the disappearance of pain in the muscles in most cases, meningitis develops, which is a continuation of the course of the disease. Actually, to prevent the development of meningitis or to maximize it effective treatment at the very beginning of the development of the disease, it is necessary to contact an infectious disease specialist with hospitalization in the infectious department.
If the Coxsackie virus causes meningitis or encephalitis (high body temperature, vomiting, severe headaches, neck stiffness - when it is impossible to reach the chest with the chin), then you should urgently call " ambulance"and be hospitalized in the infectious diseases department. If it is impossible to call an ambulance for any reason, then you should get to the nearest infectious diseases department in your own transport as soon as possible.
If the Coxsackie virus causes an infection like poliomyelitis (flaccid paralysis lower extremities, pain in the legs and arms, decreased muscle tone, attacks of muscle tremors, upset stool and urination), then you should contact an infectious disease specialist. If for some reason there is none, you should contact your pediatrician or therapist.
If the Coxsackie virus provokes mesadenitis (high body temperature, bouts of acute abdominal pain, constipation, enlargement of the cervical, inguinal, axillary lymph nodes), then you should contact surgeon ().
If the Coxsackie virus causes symptoms of an intestinal infection (low body temperature, vomiting, diarrhea, dry skin and inflammatory process in the upper respiratory tract - runny nose, pain and redness in the throat, cough), then you should contact an infectious disease specialist.
 If the Coxsackie virus provokes pericarditis or myocarditis (prolonged fever, pain in the heart, arrhythmia, shortness of breath, fainting, cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle), then you should be hospitalized in a hospital under supervision cardiologist () or a therapist.
If the Coxsackie virus provokes pericarditis or myocarditis (prolonged fever, pain in the heart, arrhythmia, shortness of breath, fainting, cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle), then you should be hospitalized in a hospital under supervision cardiologist () or a therapist.
If the Coxsackie virus provokes catarrh of the upper respiratory tract (high body temperature, runny nose, pain and redness of the throat, cough, hoarse voice, etc.), then you should contact a general practitioner, or a pediatrician in the case of a child.
If the Coxsackie virus provokes hemorrhagic conjunctivitis (redness and pain in the eyes, swollen eyelids, lacrimation, photosensitivity), then you should contact ophthalmologist () so that he prescribes treatment and prevents possible complications.
If the Coxsackie virus occurs in the form of orchitis or epididymitis (high fever, pain in the testicles, enlargement of one or both testicles, enlargement of the inguinal lymph nodes), then you should contact an infectious disease doctor or urologist ().
Diagnosis of the Coxsackie virus. What tests can the doctor order?
With typical manifestations enteroviral infections the diagnosis can be determined on the basis of characteristic symptoms: herpangina, exanthema, hand-foot-mouth syndrome, fever. In this case, specific virological studies are often not required. But since coxsackie virus often proceeds atypically, then it is possible to prove an enterovirus infection only with the help of special laboratory tests.To identify enterovirus, two types of laboratory diagnostics are used:
1.
PCR diagnostics - identification of the virus in the biological fluids of the patient (feces, swabs of mucus from the nasopharynx, urine, and others).
2.
Serological research methods - detection of specific antibodies (immunoglobulins) to the virus in the blood.
In addition, the patient will need to additional examination:
- general blood analysis;
- general urine analysis;
- analysis of cerebrospinal fluid (if there are symptoms of meningitis);
- other types of research, prescribed depending on the lesion of a particular organ ( X-ray (book), MRI of the brain (make an appointment), ECG (sign up) And so on).
General analysis of blood and urine
AT general analysis blood with the Coxsackie virus, there are changes typical of many viral infections (moderate increase in leukocytes due to lymphocytes, accelerated ESR). In severe cases, a decrease in the level of lymphocytes (lymphopenia) is possible.Blood test for antibodies to Coxsackie viruses
 With enterovirus infections from the first days of the disease, human immunity reacts with the formation of specific antibodies, or immunoglobulins. They are detected by serological blood tests.
With enterovirus infections from the first days of the disease, human immunity reacts with the formation of specific antibodies, or immunoglobulins. They are detected by serological blood tests. Coxsackie virus markers:
- Class M immunoglobulins (IgM) to Coxsackie viruses - antibodies of the acute period of the disease;
- Immunoglobulins of class G (IgG) to Coxsackie viruses are antibodies of a past disease.
By using this method virus serotype cannot be determined. The accuracy of such diagnostics is more than 90%.
Treatment of the Coxsackie virus
In most cases, diseases associated with the Coxsackie virus do not require hospitalization, but there are cases when inpatient treatment is indispensable.When is it necessary to urgently call a doctor?

- The child is not yet one year old and has a high body temperature;
- Fever for more than 3 days, the temperature is poorly controlled by antipyretic drugs;
- The child has not eaten or drunk for more than 24 hours;
- Loss or confusion of consciousness, delusional state;
- Severe weakness, constant drowsiness;
- There were signs of meningitis (severe headaches, vomiting, convulsions, and others);
- "Uncaused" bruises appeared on the skin;
- Repeated vomiting and diarrhea (more than 6 times a day), against which the child becomes lethargic;
- The child does not urinate for more than 12 hours;
- Severe pain in the abdomen, in young children this symptom is characterized by constant strong crying and pulling the legs to the stomach;
- Paroxysmal dry cough, shortness of breath;
- The appearance of cyanosis (cyanosis of the skin of the face and extremities);
- Suspicion of paralysis of the muscles of the limbs.
How to treat the Coxsackie virus at home?
1. Required bed rest to normalize body temperature and general well-being. 2. Plentiful drink- a prerequisite for the treatment of enteroviral viral infections. The child should drink often and a lot, it can be anything - water, tea, fruit drink or compote.
2. Plentiful drink- a prerequisite for the treatment of enteroviral viral infections. The child should drink often and a lot, it can be anything - water, tea, fruit drink or compote.
Acyclovir for Coxsackie virus
Acyclovir is an antiviral drug used for herpes infections. Coxsackie virus has nothing to do with herpes viruses, therefore, acyclovir is not used for enterovirus infections and is absolutely ineffective.Consequences and complications of enterovirus infections
 Any infectious pathology has a risk of complications. Since the Coxsackie virus is very diverse, the complications can be very diverse. It all depends on which organs are affected by the virus.
Any infectious pathology has a risk of complications. Since the Coxsackie virus is very diverse, the complications can be very diverse. It all depends on which organs are affected by the virus. The most dangerous complication of the Coxsackie virus is cerebral edema, which always threatens the patient's life and requires resuscitation.
Possible complications and consequences of the Coxsackie virus:
1.
Cerebral edema.
2.
Accession bacterial infections: sinusitis, bronchitis, pneumonia, purulent conjunctivitis, purulent meningitis, etc.,
Why is the Coxsackie virus dangerous for a woman during pregnancy?
- The possible development of a severe course of enterovirus infection with damage to the nervous system, heart and other organs;
- high risk of life-threatening complications of the disease;
- miscarriage (miscarriage), premature birth.
How dangerous is the Coxsackie virus for the fetus?
- Intrauterine infection of the fetus;
- the development of anomalies in the development of the central nervous system of the child (anencephaly - the absence of the cerebral hemispheres, hydrocephalus - dropsy of the brain, and other severe pathologies);
- intrauterine growth retardation and pregnancy fading;
- intrauterine fetal death.
What is dangerous enterovirus infection for a newborn baby?
Group B coxsackievirus is most dangerous not during pregnancy, but during and immediately after childbirth. In newly born children, the risk of infection with the Coxsackie virus is very high. Neonatal encephalomyocarditis may develop, in which there is a high mortality (about 40% of cases) and a high risk of developing severe neurological pathologies.
Interesting that if a newborn child was not infected immediately after birth, but after a while, and receives breastfeeding, then the risk of infection is practically absent. This is due to the mother's antibodies she passes on with her milk.
In what trimester of pregnancy is the Coxsackie virus most dangerous?
Enteroviral infections are undesirable throughout pregnancy. On the early dates there is a risk of miscarriages and fetal abnormalities, since all organs and tissues of the fetus are only being laid and formed. But in the later stages, the risk of developing enterovirus infections in a newborn increases, which also has negative consequences for the health and life of the child.
What to do if a pregnant woman becomes infected with the Coxsackie virus?
First, do not panic, in most cases, enterovirus infection does not become a tragedy for the expectant mother and child. Often it proceeds as SARS, herpetic sore throat or exanthema. Such women are usually hospitalized in a hospital and monitor the condition of the patient herself and her baby. Of the treatment, Paracetamol and detoxification therapy are usually prescribed (enterosorbents, infusion solutions in the form of droppers, vitamins, etc.). You will have to regularly take stool tests to determine the virus carrier, blood to control the production of antibodies, and monitor the ultrasound of the fetus.
How contagious is a patient with the Coxsackie virus? Quarantine for enterovirus infections
 The beginning of virus isolation is 1-2 days before the onset of the disease, and the "peak of infectivity" falls on the 2-3rd day of the disease. After recovery, the patient is excreting enteroviruses for several more weeks, in rare cases - several months and even years. During illness, all body fluids are contagious, but more prolonged release virus is observed with feces.
The beginning of virus isolation is 1-2 days before the onset of the disease, and the "peak of infectivity" falls on the 2-3rd day of the disease. After recovery, the patient is excreting enteroviruses for several more weeks, in rare cases - several months and even years. During illness, all body fluids are contagious, but more prolonged release virus is observed with feces. If a child who attends Kindergarten or school, then the baby must be isolated for the entire period of the disease, and allowed into the children's team only after complete recovery, normalization of body temperature and cleaning of the skin from rashes, but not earlier than after 14 days. For serous meningitis, children are isolated for 21 days.
Quarantine in the children's team is usually announced for 14 days, this is how long the incubation period can last. If during this time new patients are detected, then the quarantine is extended for another 14 days.
After identifying a patient with an enterovirus infection in children's institutions, final disinfection is mandatory, and sanitary and epidemic services are usually involved in this.
Also, quarantine is imposed on maternity and children's departments in which sick children, parents or medical personnel were identified.
Immunity after the Coxsackie virus
After an enterovirus infection, specific antibodies to the virus are formed in the human body, which protect against re-infection. That is, a strong immune system is developed. But such antibodies are effective only against those serotypes of the virus that a person has been ill with. Recall that there are 29 Coxsackievirus serotypes and 32 ECHO serotypes. Therefore, repeated enterovirus infections caused by "new" virus serotypes are possible.Prevention of enterovirus infection
A vaccine against Coxsackie viruses (specific prophylaxis) does not currently exist, this is due to the large number of serotypes and the variability of the virus.What to do if a child is sick with the Coxsackie virus?
- It is desirable to isolate the patient from other children in a separate room;
- carefully monitor the cleanliness of the hands of all family members;
- regularly carry out wet cleaning, disinfection of pots and toilets, wipe door handles, ventilate rooms;
- for disinfection, disinfectants containing active chlorine, hydrogen peroxide, 0.3% formalin solution are used;
- quartz lamps are effective, but people should not be allowed to stay in the room where quartzing takes place, and after the procedure, thorough ventilation is necessary;
- allocate separate dishes for the patient, it must be processed;
- toys, towels and various "common use" items will have to be processed;
- for contact children, the introduction of gamma globulin is recommended, which will enhance protection against the Coxsackie virus and its severe manifestations, and for children with weakened immunity, the use of interferon preparations and immunostimulants is recommended;
- Intestinal infection - description, types, ways of infection, symptoms (diarrhea, vomiting, temperature). Rotavirus infection in a child and an adult - symptoms and treatment
- Coxsackie virus - description, incubation period, symptoms and signs of enterovirus infection in children and adults, photo. How can a child become infected with the Coxsackie virus?