Syphilis is an infectious disease caused by the microorganism Treponema pallidum, or pale treponema. The pathogen enters the human body through damaged skin or mucous membranes. Transmission of the microorganism through the placenta and through blood transfusion is possible.
Skin manifestations of syphilis
Skin manifestations can be a sign of primary syphilis, when the microbe multiplies directly at the site of penetration. This forms a hard chancre.
When treponema spreads through the bloodstream, the body begins to fight the infection and produces antibodies. When the microbe interacts with immune system biologically isolated active substances leading to the development of manifestations of secondary syphilis. One of these signs is a syphilitic rash.
Tertiary, or late syphilis, occurs after long time after infection. It is accompanied by damage to the bones, nervous system and other organs. A rash with syphilis in the late period is one of the frequent manifestations of the disease.
Skin manifestations accompany the congenital form of the disease.
In each phase of the disease, rashes with syphilis have their own characteristics.
Primary syphilis
The first symptoms of a syphilitic rash appear at the end of the incubation period, which on average lasts from 2 weeks to 2 months. A defect with a diameter of 2 mm to 2 cm or more appears on the skin or mucous membrane. The primary lesion is called a "hard chancre" and looks like a rounded ulcer with even edges and a smooth bottom, often saucer-shaped.
The ulcer is painless, the discharge from it is insignificant. It is located on a compacted area - an infiltrate. It is very dense and resembles thick cardboard, cartilage, rubber to the touch.
Erosion is similar to an ulcer, but does not have well-defined edges. This is a superficial defect that can go unnoticed. A hard chancre or erosion is most often single, but several foci may form.
Small ulcers are more common in women and are located on mucous membranes. Giant chancres up to 5 cm in diameter are localized on the skin of the abdomen, inner thighs, perineum, chin, upper limbs (hands and forearms) and are recorded mainly in men.
A hard chancre can be located on the lips or on the tongue. In the latter case, a slit-like or stellate form of the defect occurs.
In the focus of damage, treponema intensively multiply, so the primary chancre can serve as a source of infection for other people. The ulcer persists for about 7 weeks, after which it heals with a scar.
congenital syphilis
With early congenital syphilis, which manifests itself soon after birth, typical secondary syphilides are often observed. However, this form of the disease is characterized by special skin manifestations.
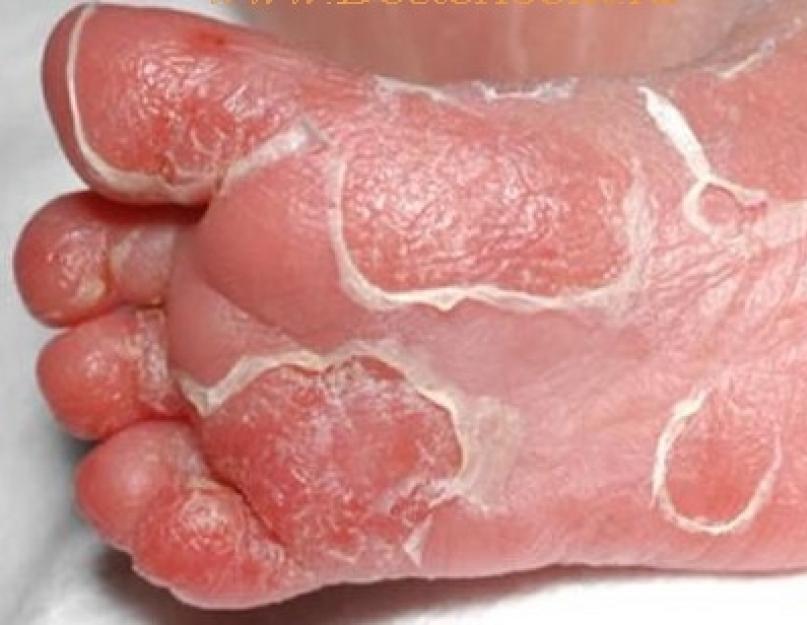
Papular syphilide may be represented by skin infiltration. The skin thickens, reddens, swells, then peeling begins. This sign appears on the palms, soles, buttocks, as well as around the mouth and on the chin. The affected skin is damaged with the formation of diverging cracks. After their healing, scars remain for life. Amazed nasal cavity and vocal cords.
Syphilitic pemphigus is another typical manifestation of congenital syphilis. Bubbles with transparent contents, up to 2 cm in size, surrounded by a red rim, form on the skin. They usually appear on the palms and soles. Bubbles do not increase and do not merge. At the same time, the internal organs suffer, the general condition of the child worsens significantly.

syphilitic pemphigus
In the late period of the congenital form of the disease, gummous and tubercular formations (syphilides) typical of the Tertiary period are found.
Diagnosis and treatment
How to determine what caused skin changes? When rashes of unknown origin appear, you should consult a dermatologist. In many cases, the diagnosis becomes clear on examination.
To confirm the syphilitic cause of the disease, additional studies are carried out:
- detection of treponema in discharge from hard chancre or erosions;
- non-treponemal tests (microprecipitation reaction or rapid reaction with plasma);
- treponemal tests (immunofluorescence reaction, treponema immobilization reaction);
- enzyme immunoassay (passive hemagglutination reaction).
Laboratory diagnosis of syphilis is quite difficult. It is difficult to interpret the results on your own, so you need to consult a doctor.
Skin manifestations of syphilis can occur on the upper or lower limbs infected if the disease has developed to a secondary form or has been transmitted by household means.
Multiple rash with syphilis
At the secondary or tertiary stage of infection, syphilis on the skin can appear as a multiple inflamed rash in the chest and upper limbs cause itching, pain and burning.
Multiple syphilitic chancres on the body
Skin rashes with syphilis can take the form of multiple inflamed ulcers, from which lymph or purulent discharge constantly oozes.
Syphilitic rash in children

If the disease had an innate nature of penetration into the body, skin syphilis takes the form of a multiple rash in the neck and forearms of a sick person.
Chancres in the transitional stage of syphilis

It should be noted that the primary skin rashes with syphilis, the photos look like a small amount of ulcerative lesions with smooth edges. These do not leave scars or scars after healing and do not cause any discomfort to the carrier of the infection.
Skin manifestations of syphilis photo ulcers
In rare cases, syphilis skin photo may be characterized by purple or purple spots with a dark blood bottom. These ulcers often exude blood or pus.
Skin manifestations of syphilis photo on the abdomen

IT'S IMPORTANT TO KNOW!
In some advanced cases, infection can provoke the so-called marbled skin with syphilis. This means that lesions on the abdomen or back will crust over and coalesce into one large lesion that is difficult to remove and cure.
Eruptions on the scrotum
With sexual transmission of syphilis, symptoms on the skin of an infected man may appear on the penis or scrotum in the form of a multiple or single rash, papules.
Purulent syphilitic eruptions

In addition to chancres and papules, the manifestations of syphilis on the skin also often take on the character of watery papules or abscesses that can be confused with a skin fungus or an allergic rash.
Chancres on hand
With a household method of infection, syphilis rashes on the skin often appear on the hands or in oral cavity infected. In this case, the wounds look like large purulent abscesses or blisters.
Nasal lesions in syphilis
Depending on the stage of development of syphilis, spots on the skin can take the form of deep purulent ulcers that are not easy to eliminate with medicinal or bactericidal effects.
Multiple rashes on the body

It is not uncommon for an infected person to have multiple acneiform rashes on the back or abdomen, which cause inflammation of the skin and may cause discomfort to the host.
Sexual syphilis
With sexual transmission, the infection often manifests itself in the genital area in the form of small purulent abscesses or round wounds of the correct form.
Weeping chancre
In rare cases, the initial signs of syphilis may release lymph or pus when they appear on the skin. This type of damage is dangerous and contagious to others.
Purulent wounds on the face
In the elderly, it can develop on the face and lead to deep skin lesions, purulent abscesses and wounds.
BOOK YOUR APPOINTMENT:

Red spots with syphilis are a rather unpleasant phenomenon, and sooner or later they occur in an infected person, especially if timely treatment is neglected. The nature and size of the spots can be completely different, the same can be said about the timing of their appearance - there are no absolute guarantees after what period of time the rash will appear.
This article will focus on the stages of syphilis and the skin manifestations characteristic of these stages, in addition, we will learn a little general information about this disease and get acquainted with the methods of its diagnosis.
The causative agent of syphilis is called "pale treponema". It is a gram-negative spirochete, which gets its name from the fact that it stains pale pink color when using the Romanovsky-Giemsa method.
Syphilis is a chronic systemic sexually transmitted infection that affects the skin, mucous membranes, internal organs, bones and nervous system. In Russia, the disease was first recorded in 1499. Like most serious pathologies, syphilis has its own classification.
The following groups are distinguished:
- primary;
- secondary (early and late);
- tertiary;
- congenital.
Note! It was found that the early forms of syphilis are more contagious, syphilis can be resolved without a trace. In late forms, the degree of contagiousness is less, however, syphilides are accompanied by irreversible destruction of body parts.
In more advanced classifications, syphilis can also be:
- seronegative;
- seropositive;
- fresh;
- hidden;
- recurrent;
- active;
- early or late congenital;
- visceral;
- nervous system;
- fetus.
Cases in which there is fetal syphilis, or congenital syphilis, almost always end in the birth of a dead child, or the death of a child in the womb.

Transmission routes
Almost all known routes of transmission are available for this disease, and therefore the incidence of syphilis among the population is steadily increasing.
Known routes of transmission include:
- Sexual- the disease is transmitted by contact with an infected person, the risk of infection is about 50%. Syphilis is transmitted through all types of sexual contact.
- Domestic- occurs when one of the partners is infected, and the second is not aware of it, or neglects the rules of hygiene. Infection occurs through objects of common use, saliva during kissing.
- Blood transfusion- cases of infection are observed during the transfusion of blood infected with syphilis to a healthy person. However, this is a very rare occurrence, because. The donor is carefully screened before donating blood. More often, this route of infection occurs in injection drug addicts, when using one syringe.
- Transplacental- consists in the transmission of syphilis to the child from the mother through the placenta during pregnancy. Leads to congenital syphilis. In addition, infection can occur during breastfeeding or passage through the birth canal.
- Professional- meets at medical workers that come into contact with the body fluids of a sick person. A doctor can become infected during a surgical operation if there was damage to the skin in the process.
From the information received, it follows that in order to avoid infection, one should not neglect protection during sexual intercourse, and also use an individual set of dishes and hygiene products when living with a patient with syphilis.

The characteristic rash of syphilis
Spots on the body are an integral part of the manifestations of syphilis. The disease begins with the formation of a primary affect - a hard chancre, which is a hard, painless, deep ulcer.
The chancre is not soldered to the surrounding tissues, does not bleed, and does not increase in size. In the future, the course of primary syphilis is not accompanied by any changes in the skin or mucous membranes.

With the development of the disease and its transition to secondary syphilis, spots from syphilis occur approximately 1-2 weeks after the prodromal symptoms. The rash in this period is characterized by polymorphism and a benign course (they do not destroy surrounding tissues), the absence of subjective symptoms (sometimes slight itching) and signs of acute inflammation.
With syphilis, the occurrence of syphilitic roseola or spotted syphilis is noted. In this case, the elements have a rounded shape, a diameter of up to 10 mm and a pale pink color. Syphilis spots are localized on the skin of the trunk, arms and legs, in rare cases on the face, feet and palms. The appearance of roseola occurs gradually, about 10 pieces per day, and when pressed on them, they disappear.
Papular syphilide is another type of rash, the elements look like densely elastic pinkish or red papules, no larger than 5 mm in size. Over time, peeling begins in the center of the papule, with further spread to the periphery. After resolution, hyperpigmentation is present at the site of the papule for a long time.
Note! A typical sign of syphilis is the presence of "Biett's collar" - peeling along the edges of the papule, when it is already absent in the center.
What are the spots on the body with syphilis in rarer forms of skin manifestations?
This includes pustular syphilis, which appears mainly in debilitated patients and is accompanied by purulent exudate, after which a yellow crust forms after drying. Another manifestation of a rare form of rashes is pigmented syphilis, which is formed on the back and sides of the neck and has rounded white spots. This sign is called the "necklace of Venus".
With tertiary syphilis, the development of tertiary syphilis occurs over several years, without any sensation or inflammation. Elements of rashes in this period leave behind scars.
There are gummy and tubercular syphilides:
- Tubercular syphilides characterized by the formation of infiltrative nodules that protrude above the skin, no larger than 7 mm in size. The nodules are red-brown in color and firm to the touch. Rashes are arranged asymmetrically, the elements are at different stages of development, but do not merge with each other.
Over time, syphilides become necrotic and rounded ulcers are formed that have a clean bottom, smooth edges and an infiltrated base. Ulcers with syphilis heal for a long time, leaving behind areas of atrophy or scars with hyperpigmentation along the edges. In the area of scars, repeated rashes never occur.
- Gummous syphilis- usually a single element, which is a node located in the subcutaneous tissue and painless on palpation. Gummas can be located on the forehead, in the area of the elbow or knee joints, on the shins or forearms.
At the first stages, gumma is mobile, but later, due to an increase in size and fusion with surrounding tissues, it loses its mobility. Further, a hole is formed in the center of the node, through which a liquid is separated, of a gelatinous nature.
Characteristic for gumma is the formation of a crater-like pit with a necrotic rod at the bottom. After the rod leaves, the ulcer begins to heal with the formation of a retracted star-shaped scar.
Sometimes there are cases in which the gumma does not turn into an ulcer, then the node decreases and is replaced by dense connective tissues. Gummas can form and affect not only the skin and subcutaneous fat layer, but also penetrate into cartilage, tissues, blood vessels and muscles, destroying them along the way.

Diagnosis of manifestations of syphilis
The appearance of any skin rash usually causes anxiety, even if it is a contact allergy, and not a serious sexually transmitted disease. In any case, if a rash appears and syphilis is suspected, it is necessary to seek advice from a dermatovenereologist. After that, a diagnostic method will be individually selected and instructions will be explained on how to properly prepare for the study.
The selection of the research method is carried out on the basis of an anamnesis and existing symptoms:

It is worth noting that the price of some tests can be quite high, so you should not engage in self-diagnosis, but rather contact a specialist so that he not only directs you to the necessary tests, but also interprets the results.
From the photos and videos in this article, we managed to learn a little more about syphilis, as well as all the possible variations of the rash with this disease.

Frequently asked questions to the doctor
Real experiences
Hello. A week ago I had unprotected intercourse, and a couple of days later I noticed a red rash on my partner's body. Could this be a sign of syphilis, and should I get tested now?
Good day. During syphilis, certain periods are distinguished. The initial one is called primary syphilis. At the stage of primary syphilis, there is a certain period of time, namely, the first 3-4 weeks after infection, when the test results do not reveal the disease. This period is called primary seronegative syphilis.
According to statistics from the Ministry of Health, In Russia, there are 30 syphilis patients per 100,000 inhabitants. These figures are not indicative, since a large number of infected people do not go to doctors for treatment. Thus, the risk of infection remains high.
A little about syphilis
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection. The causative agent of this disease is pale treponema, which is a bacterium that is capable of movement.
How does syphilis appear on the skin?
Syphilitic manifestations are very diverse and cause difficulties in differential diagnosis syphilis with other skin diseases. Morphological elements that appear on the skin with syphilis vary depending on the stage of the process.
The incubation period of this disease is on average from 2 weeks to 2 months. Shortening of terms occurs in people with reduced immunity who have undergone infectious diseases, with a history of cancer, tuberculosis, HIV infection.
During these periods, the pathogen is in the human body, but its concentration is not enough to cause symptoms of the disease. There are no skin manifestations.
After the specified time period, when there was an accumulation of pale treponema, the stage of primary syphilis develops. It is characterized by a single, but most contagious skin manifestation - a hard chancre.
It is formed, as a rule, at the site of penetration of pale treponema (with genital contact - in the genital area, with oral - genital contact - in the oral cavity, in the lips, etc.).
The formation of the chancre occurs in several stages:
- the formation of a spot of small size, pink-red;
- formation of an erosive defect;
- erosion bottom compaction, color change to bright red. Erosion is covered with a transparent or brown film.
With timely treatment or, on the contrary, the transition to the next stage of syphilis, the chancre again passes into the spot stage, and then completely disappears. As a rule, such a neoplasm does not cause discomfort in an infected person. There may be mild itching in the area of erosion.
A syphilitic rash is a modification of the superficial vessels of the skin. Pale treponema, entering the bloodstream, releases specific toxins that dilate blood vessels. Further, the vascular reaction depends on the state of immunity. Each person is individual, and his immune response, respectively, too.
Simple vasodilation on the skin manifests itself in the form of spots (roseol). Such spots easily disappear when pressed (the vessels are compressed, and the skin becomes pale).
If there is an increase in the permeability of the vascular wall, plasma partially accumulates around the vessel along with immune cells, an inflammatory reaction occurs, and a hard "muftka" is formed around the dilated vessel.
On the skin, this manifests itself in the form of a small rounded induration, i.e. a nodule (papule) is formed.
If the immune system is weakened, bacteria begin to actively multiply outside the vascular bed. Immunity, protecting the body, forms an inflammatory capsule around the largest accumulations of bacteria, inside which pus accumulates. Such a manifestation immune response on the skin looks like pustules (pustules).
Syphilis is a classic sexually transmitted (i.e., sexually transmitted) disease that affects males and females equally. Mostly they get syphilis at reproductive age: men from 16-18 to 65-70 years old, women from 16 to 35-45 years old.
Most people believe that syphilis can only be contracted through sexual contact, and if a man or woman keeps intimate relationships clean, this disease does not threaten them.
This opinion is erroneous, since the transmission of infection is possible both through contact and through medical procedures in dubious institutions where sterility conditions are not observed.
Dangerous and direct blood transfusion, which is resorted to in emergency cases: the donor may not know about his illness, which will lead to infection of the recipient.
The third way is from an infected woman to her child.
Classification
After the disappearance of the primary hard chancres and the development of the secondary stage, new rashes begin to cover the body. The rash on the body with secondary syphilis is very diverse

- Roseola - pale pink spots, most often covering the abdomen and side of the body of the patient. They do not have clear contours, do not merge, do not cause discomfort. Roseola is considered the most common type of rash, as it is observed in 90% of Lewis patients.
- Papules are round nodules, no larger than a pea. The first days after formation are smooth, but after that they can peel off. A papular rash with syphilis is usually observed on the palms, feet, in anus and on the genitals.
- Palmar-plantar syphilis is another type of papules, characterized by clear contours and a typical color - bright red or purple. It affects mainly the palms and soles of the feet. Sometimes they are confused with corns, which is why people put off visiting the doctor. A few days after formation, they crack and begin to peel off.
Syphilis can affect any organs and systems, but the manifestations of syphilis depend on the clinical period, symptoms, duration of illness, age of the patient, and other variables. Therefore, the classification seems a little confusing, but in reality it is built very logically.
- Depending on the length of time that has passed since the moment of infection, early syphilis is distinguished - up to 5 years, more than 5 years - late syphilis.
- According to typical symptoms, syphilis is divided into primary (hard chancre, scleradenitis and lymphadenitis), secondary (papular and pustular rash, spread of the disease to all internal organs, early neurosyphilis) and tertiary (gum, lesions internal organs, bone and joint systems, late neurosyphilis).

chancre - an ulcer that develops at the site of introduction of the causative agent of syphilis
- Primary syphilis, according to the results of blood tests, can be seronegative and seropositive. Secondary according to the main symptoms are divided into stages of syphilis - fresh and latent (recurrent), tertiary are differentiated as active and latent syphilis, when treponemas are in the form of cysts.
- By predominant damage to systems and organs: neurosyphilis and visceral (organ) syphilis.
- Separately - fetal syphilis and congenital late syphilis.
There are such types of rashes with syphilis:
- First stage. The manifestation of this stage can be seen a month after the infection was introduced into the body. At this point, you can observe the first signs of syphilis. The rash is manifested by red pimples, which after a certain time take the form of sores. The rash may disappear after a couple of weeks, but will reappear soon after. Such a rash can stay on the human body for a long time, even be present for several years.
What are the stages
There are several stages that patients with syphilis go through:

What are the periods of the disease? They are distinguished depending on the duration of the disease and the prevalence of the lesion.
- primary syphilis. it initial stage illness. It is characterized by the appearance of a hard chancre and an increase in lymph nodes.
- Secondary syphilis. Microorganisms spread throughout the body via the hematogenous route. As a result, a typical rash appears on the skin.
- Tertiary period. Here, the formation of specific tubercles on the skin and in the internal organs is already taking place.
- Hidden. A special variant of the pathology, in which there is only laboratory confirmation of the disease, but there are no external manifestations.
- congenital pathology. This is a variant of the disease that is diagnosed in newborns.
What are the manifestations of different stages disease?
Various Clinical signs depends on the degree of activity of the microorganism. What are the skin manifestations of syphilis?
Primary Period
In this period, the main symptom is a hard chancre. The duration of this period is about two months.
A hard chancre is formed in the place where the introduction of pale treponemas occurred. First, erythema with clear boundaries appears in this area.
Soon it transforms into a small seal that rises above the surface of the skin. After some time, erosion or an ulcer forms on this seal.
Hard chancre has certain signs:
- bright red or copper color;
- if it is erosion, then its bottom is varnished and shiny;
- if it is an ulcer, its bottom has a yellowish color;
- the edges of erosion are clear, the ulcers are sloping;
- the shape of the defect is oval or rounded;
- there are no signs of inflammation on the skin;
- there is no soreness.
Most often, the defect is localized in the genital area. However, other areas of its occurrence are also possible.
Secondary period

Secondary syphilis begins two months after the formation of a hard chancre. At this stage of syphilis, various rashes form on the skin. All of them have characteristic features:
- have a benign course - disappear on their own even without treatment, do not leave scars;
- the patient's well-being does not suffer, there are no subjective sensations;
- there are no manifestations of inflammation;
- the rash is characterized by polymorphism - that is, at the same time, different types rashes;
- all rashes are contagious, that is, they contain microorganisms.
Most often in this period, spotted syphilis is observed. It is also called syphilitic roseola. A rash forms on the trunk and limbs. Its elements are small spots. They have their own characteristics:
- a rash is formed gradually and finally develops by the tenth day;
- the spots are light pink in color;
- rashes are quite abundant, arranged chaotically, not prone to merging;
- have a rounded shape, are at the level of the skin;
- not prone to peeling.
When diagnosing, it is required to distinguish this condition from measles and rubella, different types depriving.
The second most common type of rash with syphilis in the secondary period is papular syphilis. It has several varieties.
- Lenticular syphilis. It is represented by dense elastic papules with clear boundaries. They are often dark red in color with a bluish tinge.
- Miliary syphilis. Represented by small papules the size of a millet grain, having a red color. They are grouped on the skin in such a way that they form different shapes.
- Numular syphilis. This rash with syphilis is represented by large rounded papules. They are dark red in color. After their disappearance, pigmentation remains.
- Weeping syphilis. Rashes are located in large folds of the skin. The papules are small, merge and form a weeping surface.
- Plantar-palmar syphilis. Syphilis on the skin with this option looks like purple or yellow spots. They quickly thicken and become covered with scales.
- Wide warts. These rashes are represented by small papules, on the surface of which vegetations form. They are found in skin folds and in the genital area.
Secondary syphilis lasts for several years.
Tertiary period

late stage of the disease. The main manifestations are damage to internal organs. However, there are also signs of the disease on the skin. What are they represented by?
Signs of a syphilitic rash
 in the photo the first signs of a syphilitic rash on the abdomen
in the photo the first signs of a syphilitic rash on the abdomen 
With the disease in question, the spots on the patient's body differ in several ways. characteristics, among which are the following:
- Rashes, as a rule, are not localized on a specific area of the body, they can appear anywhere.
- The affected areas do not itch, do not itch and do not hurt, there is no peeling on them.
- The elements on the body are dense to the touch, round in shape, can be single or merge with each other.
- A syphilitic rash may be pink or red with a blue tint.
- After the disappearance of the rash, no traces or scars remain on the skin.
The attached photo clearly shows what a syphilitic rash looks like, which is difficult to confuse with any other.
Symptoms in women
 in the photo, the manifestation of syphilis in women on the lips
in the photo, the manifestation of syphilis in women on the lips 
In women, as in men, there are three stages of syphilis: primary, secondary and tertiary. The disease progresses gradually incubation period in women, it often lengthens due to various factors, such as taking antibiotics.
Differential Diagnosis
Differential diagnosis of secondary syphilis includes a wide range of skin diseases and acute infections. It is easy to confuse a roseolous rash with rashes with measles, typhoid fever, rubella and typhus.
However, unlike the listed diseases, the general condition of the patient is not disturbed and there are no symptoms of damage to internal organs.

Syphilides are differentiated from skin diseases, which are often accompanied by itching, soreness and pronounced signs of skin inflammation. Finally, microscopic and immunological examination of the discharge / scraping from papules allows them to be finally distinguished from each other.
For syphilis, they contain a large number of mobile pale treponemas.
Syphilitic alopecia is differentiated from androgenetic alopecia and fungal infections of the scalp. In the first case, there is a normal content of sex hormones in the blood and positive analysis for syphilis.
Unlike fungal alopecia, the scalp with secondary syphilis does not peel off, there are no signs of inflammation and spores of the fungus.
If a person develops unknown skin rashes, then a dermatologist should be consulted to determine the origin of the symptoms. Often a patient examination is sufficient to make a preliminary diagnosis. To confirm the presence of syphilis in a person, it is necessary to carry out the following diagnostic procedures:
- Inspection for the presence of treponema in the fluid that is separated from erosions or from a hard chancre.
- Tests that also concern treponemas. These are the immobilization reaction and the immunofluorescence reaction.
- Tests that are not related to treponema. This is a fast plasma reaction or a microprecipitation reaction.
- Passive hemagglutination reaction or enzyme immunoassay.
It is difficult to assess the results of such studies. Here you can not do without consulting a doctor, since the laboratory determination of the presence of syphilis is very difficult.
Treatment
A syphilitic rash is only part of the manifestation of the disease. The main development of the disease occurs inside the body, where almost all internal organs are affected.
Therefore, it is impossible to cure only a rash with ointments and creams without eradicating the disease from the inside. The treatment of syphilis is a course of injections of penicillin, and for each form and each period of the disease it is individual.
- Incredible… You can cure syphilis, gonorrhea, mycoplasmosis, trichomoniasis and others venereal diseases forever and ever!
- This time.
- No antibiotics!
- This is two.
- During the week!
- It's three.

An effective remedy exists. Follow the link and find out what the venereologist Sergei Bubnovsky recommends!
Timely and correct initiation of treatment guarantees a minimum of complications and damage to internal organs. Treatment of syphilis should begin immediately after the first rash appears.
In order to make a correct diagnosis and develop effective scheme treatment, it is necessary to be examined by a venereologist. Treatment should be carried out according to the type of rash and the stage of development of the disease, and also be comprehensive.
That is, therapy is aimed at eliminating pale treponema from the inside and removing characteristic symptoms- rashes. The treatment complex for syphilis includes: antibiotic therapy, increased immunity, vitamin therapy.
Pale treponema is a bacterium that for half a century has remained sensitive to penicillins, which provide 100% success. Intravenous administration is carried out aqueous solutions this means for constant support in the blood of this antibiotic, which has a detrimental effect on the pathogen.
The drug is administered every 3 hours for one day, so the treatment should be carried out in a hospital. A single injection is not able to provide a complete cure.
With the shortest treatment regimens, 2-3 times the introduction of penicillins or other antibiotics effective against pale treponema is carried out.
Immunotherapy is also important during the treatment of syphilis, as the risk of catching other sexual and not only infections increases. The use of Pantocrine, Eleutherococcus extract, Pyrroxan, Methiuracil, Levamisole, etc., can increase the protective functions of the body.
Treatment of syphilis is carried out taking into account the clinical stages of the disease and the susceptibility of patients to drugs. Seronegative early syphilis is treated more easily; with late variants of the disease, even the most modern therapy is not able to eliminate the consequences of syphilis - scars, organ dysfunction, bone deformities and disorders of the nervous system.
Two main methods of treatment of syphilis are used: continuous (permanent) and intermittent (course). In the process, control tests of urine and blood are required, the well-being of patients and the work of organ systems are monitored. Preference is given complex therapy which includes:
- Antibiotics (specific treatment for syphilis);
- General tonic (immunomodulators, proteolytic enzymes, vitamin-mineral complexes);
- Symptomatic drugs (painkillers, anti-inflammatory, hepatoprotectors).
Assign nutrition with an increase in the proportion of complete proteins and a limited amount of fat, reduce physical exercise. Prohibit sex, smoking and alcohol.
Psychotrauma, stress and insomnia adversely affect the treatment of syphilis.
Treatment of secondary syphilis is essentially simple, but requires strict adherence to the dose of antibiotic. Insufficient concentration of the drug becomes a distress signal for pale treponema, in response to which it turns into an invulnerable L-form.
It allows the microorganism to survive adverse conditions and return to a viable state after their elimination.
All methods of treatment of secondary syphilis are based on parenteral administration antibiotics penicillin series. Treatment of roseola rash is carried out on an outpatient basis with long-acting drugs.
They are administered 1-2 times a week in a course of 6-10 injections. severe forms syphilis, alopecia, late relapses are treated with daily intramuscular or intravenous injections penicillin antibiotics.
Secondary latent syphilis lasting more than six months is cured by the introduction of penicillin 4 times / day. within 20 days.
Before treating secondary syphilis, the doctor will definitely find out from the patient about allergic reactions to penicillin antibiotics. If they took place, therapy is carried out with drugs of other groups.
This disease can be treated only after consultation with a specialist dermatovenereologist, who will prescribe all the necessary diagnostic measures and adequate appropriate treatment.
Independent decision-making on admission is unacceptable medications, as well as the use of funds from traditional medicine. Treatment of syphilitic lesions of the human body is a rather lengthy process in which it is necessary to take medication continuously for several months.
And in the later stages of the disease, therapy can last several years.
Pale treponema is very sensitive to antibiotics of the penicillin series, which is why they are prescribed to all syphilitic patients. If these drugs are ineffective, they are replaced by tetracyclines, fluoroquinolones or macrolides.
Most often, the treatment of syphilis occurs in a hospital, where every three hours the patient is injected with penicillin for several weeks. The patient is also prescribed vitamin substances that help strengthen and restore immunity, which suffers from long-term treatment antibiotics.
Among the medicines that are prescribed to patients with syphilis, the following can be noted:
- Bicillin, Ampicillin, Retarpen, Azlocillin, Ticarcillin, Extencillin.
- Medicamicin, Clarithromycin, Ciprofloxacin, Ceftriaxone, Doxycycline.
- Miramistin, Doxilan, Bioquinol, Bismoverol.
Therapy of syphilis can be considered successful only if the disease does not recur for five years. It is very important to follow all the doctor's prescriptions, as well as to completely exclude sexual intercourse for the duration of medication treatment.
It is very important to comply preventive measures, avoid casual sexual intercourse, do not neglect personal hygiene and a barrier method of contraception. A patient with syphilis should have his own separate dishes, towel, razor and other accessories.
Treatment of syphilitic skin lesions consists not only in the use of topical agents, but also in the administration of specific drugs.
Local treatment is not essential. Most often, antiseptic preparations are used for treatment, antibacterial ointments with the appearance of suppuration.
The main treatment is antibacterial drugs. Depending on the period of the disease, different pharmacological groups are assigned.
You can read more about treatment in the article. Modern approaches for the treatment of syphilis
Treatment of syphilis, first of all, begins with the appointment of drugs from a number of antibiotics. Prescribe those drugs that destroy syphilis.
Penicillin antibiotics are often used for this. With the use of these drugs, you can quickly get rid of the rash caused by syphilis.
But there are cases when patients do not tolerate penicillin, and therefore for them this drug is replaced with tetracycline or macrolides.
Along with this, it is necessary to prevent a reaction to antibiotics, which can be allergic. To do this, use drugs with antihistamine action, such as Claritin.
With the formation of gums and ulcers, you can use synthomycin ointment, the drug "Levomekol" or use powder. You do not need to use an antiseptic to treat the skin around.
In general, an integrated approach is used to treat syphilis. To prescribe drugs, it is necessary to take into account all individual factors relating to the patient. This is his age, gender, comorbidities, stage of the disease, as well as the general condition of the patient's body.
Since syphilis is sexually transmitted, all sexual partners of a sick person are examined. They, if necessary, are also prescribed therapy.
It is necessary to take tests and undergo examinations for everyone who has had sexual contact with a person with syphilis. In this case, the examination is required for people who have had intimate relationships over the past few months.
If syphilis manifested itself for the second time, then it is necessary to examine all people who have had intimate relationships with the patient over the past year.
To achieve a good result, it is very important to start treatment in a timely manner, as well as to choose medications right. If the patient is infected with an open form of syphilis or is at its early stage, then he must be hospitalized in the hospital of the venereology department.
Or such patients are determined in a dispensary, but this must be done within the first day after the diagnosis has been established.
Taking into account which lesions prevail in the patient, he can be assigned to the hospitals of the following departments:
- venereal;
- cardiological;
- neurological;
- psychiatric;
- therapeutic.
In addition, it is necessary to prescribe treatment to persons who have had close contact with an infectious patient. In this case, the contact could be domestic.
It is also necessary to assign preventive treatment pregnant women who previously suffered from syphilis and children born to mothers who previously suffered from this disease.
Such treatment can be obtained in the dermatovenerological dispensary.
Throughout the entire period of treatment in the patient's blood, it is necessary to maintain the level of antibacterial agents at the proper level. The treatment of such a disease is long, it will take several months. During treatment, patients are prescribed the following drugs:
- antibiotics;
- immunomodulators;
- vitamins;
- probiotics.
As you can see, the main treatment is antibiotics. To date, the most commonly prescribed antibiotics are the penicillin series.
If the disease is in the second or third stage of development, then iodine, bismuth or bismoverol are added to penicillin. At a time when the causative agent of the disease is resistant to antibiotics, and the patient is at the same time in the third stage of the disease, such agents as arsenic derivatives - Novarsenol or Miarsenol, as well as a bismuth derivative - Bioquinol, can be prescribed.
But the appointment of these drugs is possible when the patient's body is in good condition. These drugs are very toxic, so they can only be obtained in specialized institutions.
As for immunomodulators, T-activin or Timalin are mainly prescribed. B vitamins or antioxidants are usually used. Also, probiotics are prescribed from the first days of antibiotic use. You can use drugs such as Hilak, Linex or Lacidophil.