Content
There are a large number of different microbes that provoke diseases. These harmful organisms include herpes type 6 - a virus that affects an adult and a child. Herpes virus type six (HHV-6, HHV-6) belongs to a family of DNA-containing viruses that cause serious illness in humans. Below is detailed information about the causative agent of diseases: features, signs, complications, diagnostic measures and treatment.
What is herpes type 6
A type of herpes called HHV-6 (HHV-6) attacks only humans. This virus usually replicates in T-lymphocytes, which are responsible for the correct immune response of the body to the impact of harmful organisms. Herpes of the sixth type is classified into two types:
- Subtype A. The HHV-6A strain is rarely diagnosed. Often it affects the body of a person who has a severely weakened the immune system due to HIV infection, nerve fiber disease or hemoblastosis. Such a type 6 virus appears, both in children and in adult patients.
- Subtype B is considered more common. Its carriers are more than 90% of the adult population of the planet. Such a herpesvirus can be inactive for a long time, and then its activation begins against the background of a certain disease (pneumonia, hepatitis, encephalitis, and so on). According to pediatricians, children under 2 years of age are especially susceptible to the herpes virus of the 6th B-type. Doctors call this infection “pseudo rubella” and “sixth disease”.
Features of herpes type 6
Like any other disease, type six herpes has its own personal characteristics:
- The virus may not show up at first. After passing incubation period(1-2 weeks) the first signs of infection appear.
- Herpesvirus type 6 is different in that the body is able to develop protection against it. If a person once had this form of herpes, then in most cases a relapse does not occur or the disease will proceed unnoticed, without symptoms.
- Sometimes the human herpesvirus type 6 masquerades as other diseases, which greatly complicates the diagnosis and treatment of infection.
- Herpesvirus type six lives in cerebrospinal fluid, saliva, and vaginal secretions.
Symptoms
The herpes virus of the sixth type does not always have symptoms, sometimes the development of the infection does not give itself away at all. But sometimes a child and an adult can experience such Clinical signs diseases:
- sharp exanthema ( viral infection acute form in infants and young children);
- meningitis, acute hemiplegia;
- hepatitis;
- defeat gastrointestinal tract: nausea, vomiting, severe pain in the abdomen, diarrhea;
- febrile convulsions;
- manifestation of SARS;
- herpes sixth type causes fever;
- severe general malaise, weakness, decreased performance and memory, irritability, sleep disturbance;
- pancytopenia (deficiency of all types of blood cells);
- infectious form of mononucleosis.
In children
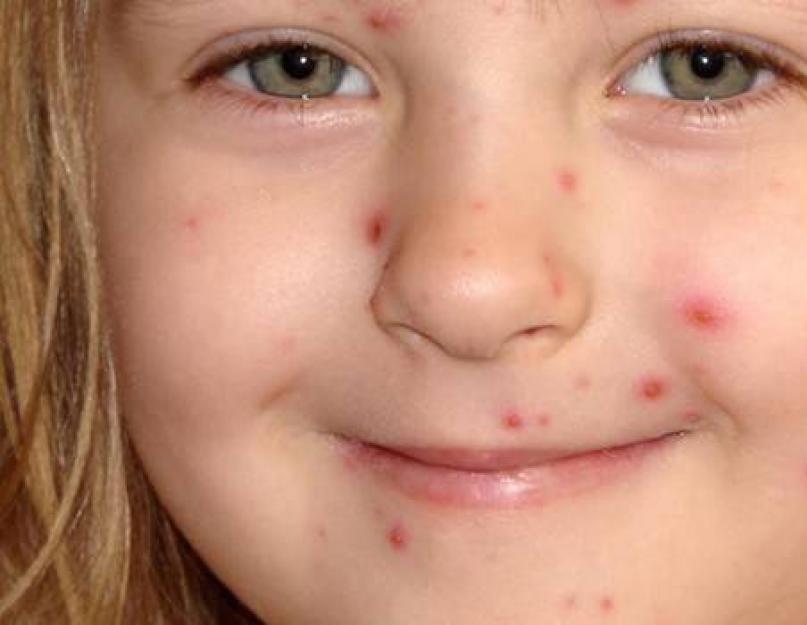
From the day the infection enters the child's body until the first signs appear, one to two weeks pass. Herpes virus type 6 in children is distinguished by its symptoms. The main symptom is a rash on the skin (roseola). She calls severe itching, scabies. This symptom appears on the back, moving to the neck, upper and lower limbs, belly. In general, the health of the little patient does not change, the appetite does not disappear, cheerfulness and normal sleep remain. The rash itself disappears in a couple of days, but after it small wounds remain on the skin (as in the photo).

There is HHV type 6 in children atypical form(no rash). At the same time, the child's temperature rises sharply (up to 40 degrees). The state of health of a patient with such a diagnosis is severe, the baby has a fever, convulsions, rolling eyes, an increase in lymph nodes. Sometimes children's HHV 6 provokes purulent rhinitis, cough, bouts of nausea and indigestion.
In adults
Doctors identify a number of symptoms that provoke the herpes virus type 6 in adults:
- a significant increase in body temperature;
- redness of the throat;
- fever, severe chills;
- diarrhea may occur;
- apathy, fatigue and weakness that does not go away for a long period of time;
- aggression, irritability.
As the infection worsens, the following symptoms may occur:
- herpes sixth type can cause dizziness;
- hypersensitivity;
- speech and vision disorders;
- shaky, unsteady gait;
- removal of arms and legs - a symptom of herpes of the sixth type;
- partial paralysis (paresis) of muscles;
- convulsions;
- coughing fits;
- herpes virus type 6 causes breathing problems;
- the appearance of a severe runny nose with pus;
- enlargement of the lymph nodes.

How is it transmitted
There are several options for infecting a person with herpes of the sixth type:
- Airborne route. Often transmitted through the saliva of the carrier, especially if in his oral cavity there are rashes.
- Another way HHV-6 enters the body is through plasma transfusion and organ transplantation.
- Interaction of a sexual type can also lead to infection if there are rashes on the genital mucosa.
- The vertical route of infection is from mother to baby in utero. In this case, the child may have serious complications chronic plan.
Diagnostics
Herpes simplex virus type 6 in children and adults is often carried out by two methods:
- PCR analysis (polymerase chain reaction). This study helps detect viral DNA.
- ELISA ( linked immunosorbent assay). This type of diagnostics refers to very accurate methods. It allows you to differentiate the DNA of herpesvirus type 6, is able to determine the initial infection or gives a chance to establish a recurrence of the disease.
Doctors do not always give directions for tests to detect a herpes infection in the body. Often the diagnosis is based on obvious external symptoms. Laboratory examinations necessary in those controversial cases when there is uncertainty about the choice of medicines for therapy or situations where the patient is in serious condition. If the examination is passed, then there are four options for decoding it:
- Immunoglobulins M and G type negative (IgM -, IgG -). No antibodies and no immune response to exposure to herpesvirus. This indicates the danger of primary infection.
- Positive M and G (IgM+, IgG+). The result signals a relapse of the disease, but the immune response is present. The doctor prescribes therapy.
- Immunoglobulins M are negative, and G are positive (IgM -, IgG +). There is an immune defense against the effects of the virus. The next outbreak of infection activity depends on the strength of the immune system.
- Positive M and negative G (IgM+, IgG -). This result indicates the primary stage of infection. Therapeutic measures appointed on an urgent basis.

Treatment of herpes type 6
When the decoding of the analyzes shows that the norm for the number of antibodies is too high, then HHV-6 requires the appointment of urgent therapy. Today, there are no medical remedies that absolutely rid the body of a child or adult of type 6 herpesvirus completely. The infection can only be brought under control through special medicines. by the most effective way antiviral chemotherapy is considered adequate therapy, and other options are less effective.
Preparations
When the disease has no complications, then the suppression of the herpes virus is carried out using complex therapy. It well eliminates the symptoms of the disease, strengthens the immune system, “lulls” the herpes virus to long time. There are five groups of modern medicines that help to cope with herpes of the sixth type:
- Immunomodulators. These drugs are needed to restore and maintain normal body defenses against viruses (Neovir, Viferon, Kipferon).
- Antiviral drugs. They do an excellent job of eliminating herpes Foscarnet (local use and local), Ganciclovir (droppers).
- Antipyretic medical supplies used when available characteristic symptoms infections, especially in case of exacerbation of herpes of the sixth type (Paracetamol, Nurofen, Analgin).
- Immunoglobulins. This group of drugs can effectively influence the production of antibodies (Amixin, Likopid, Gerpimun 6).
- It is advisable to treat herpes and through vitamins. This option is used to further strengthen the immune system. It is better to use useful complexes containing vitamins A, C, E.
Effects
Herpesvirus type six, as a rule, does not lead to death, but causes a variety of pathologies and provokes their complications. The main consequences of the disease are:
- multiple sclerosis;
- myocarditis can often be associated with herpesvirus sixth degree;
- the formation of liver failure;
- pneumonitis;
- chronic fatigue syndrome;
- cancerous tumors (leukemia, lymphoma, neoplasms in the brain);
- endocrine disorders may occur lymphatic system;
- epilepsy;
- meningoencephalitis;
- thrombocytopenic purpura;
- fulminant hepatitis.

Prevention of infection with herpes
To significantly reduce the recurrence of the "sixth" herpes and avoid the occurrence of complications, you should follow simple rules:
- More often walk in the fresh air, if possible, harden.
- Do physical exercises regularly.
- Include fresh vegetables, fruits and berries in your daily diet.
- Ensure normal regular rest, sleep well, do not overwork.
- Try not to expose yourself to the risk of contracting infectious diseases.
- Take vitamins (especially in the cold season).
Video
Attention! The information provided in the article is for informational purposes only. The materials of the article do not call for self-treatment. Only a qualified doctor can make a diagnosis and give recommendations for treatment, based on the individual characteristics of a particular patient.
Did you find an error in the text? Select it, press Ctrl + Enter and we'll fix it!Herpes strains are numerous. This is more than a hundred varieties of infection, among which only 8 have been studied. Today we will talk about such a phenomenon as type 6 herpes in adults. HHV-6 infection is harmful to the body by damaging important immune cells. The disease develops due to a weak defense system, the presence of HIV infection and hemoblastoses. For adults, the danger is a subspecies of the HHV-6A strain. Subtype B traditionally affects children with chronic fatigue syndrome.

Infection with herpes virus type 6 (class A) in adults occurs in several ways:
- Airborne. The causative agent is contained in the saliva of the carrier of the infection, which may not be aware of its own contagiousness.
- Sexual. In the presence of herpes vesicles on the genitals, a person infects his partner if barrier contraceptives are not used.
- Vertical. Thus, children become infected during fetal development, if the expectant mother has herpes. This situation is dangerous with complications for a child who has to go through an infected birth canal.
In addition, you can become infected with herpes in a clinic if an organ transplant is performed or donor blood is injected.
Symptoms of HHV-6 in adults

When infected with herpesvirus type six, symptoms in adults will resemble diseases such as influenza, tonsillitis, pneumonia. Poor health may be associated with clinical course mononucleosis.
At an appointment with a therapist or infectious disease specialist, a person complains of characteristic signs viral disease:
- Nasal congestion.
- Sore and sore throat.
- A sharp rise in body temperature to high levels.
- Enlargement of lymph nodes to the likeness of well-palpable cones.
- Muscle and joint pains, pestering in different parts of the arms or legs.
Dangerous for humans, CFS (Chronic Fatigue Syndrome) occurs as a symptom of the flu. An adult experiences a feeling of weakness and feels overtired. Lymph nodes increase on the back of the head, neck and armpits. Due to frequent headaches and temperature changes, a person feels weakened and unhealthy.
Read also: Herpes on the hands - signs and treatment
The condition is exacerbated by insomnia or anxiety. For this reason, the nervous system suffers, which is why an adult shows aggression even for a minor reason. If the body's defenses are significantly undermined, the patient develops encephalitis against the background of CFS.
Possible Complications

Herpes type 6 in adults, clinical symptoms and the methods of treatment of which we are considering in the framework of this article, in adverse conditions can seriously undermine health. It is also bad that relapses of a viral disease are asymptomatic, and therefore the carrier does not go to the doctor.
The most common complications of HSV-6:
- CNS diseases.
- Multiple sclerosis.
- Encephalitis.
- Exanthema with a weighted clinic.
- autoimmune disorders.
If an adult patient has not been able to completely cure herpes type 6 and strengthen the body, it is possible that the disease will manifest itself with severe results.
What are the consequences of infection with 6 strains of herpesvirus:
- Myocarditis.
- endocrine anomalies.
- Meningoencephalitis.
- Lymphoma of a malignant nature.
- Infectious mononucleosis.
- Liver failure.
- thrombocytopenic purpura.
- Fulminant hepatitis.
- Lymphadenitis in histiocytic necrotic form.
Attention! The presence of HSV-6 in the body predisposes to the development of AIDS. Accession to these diseases of the 7th type of herpes creates prerequisites for the formation of carcinoma on the cervix and in the nasopharyngeal tract.
Diagnosis of HSV-6 in adults

According to the patient's complaints, one can only suspect infection with herpes. To confirm the diagnosis, the patient is sent to the laboratory, where he takes a blood test for antibodies to HSV-6. Valuable diagnostic value is the dynamics of the serological study. In the first 7 days of illness, the patient's blood serum shows fluctuations in IgM levels. In the future, the analysis reflects an increase in the titer for IgG.
A general blood test reveals a change in the number of leukocytes (downward from the norm) and lymphocytes (their number increases).
The most reliable picture of the symptoms of type 6 herpes is reflected by the following diagnostic methods:
- PCR. The chain polymerization reaction detects particles of herpes simplex in the blood serum, saliva and genital smear.
- ELISA. ELISA is necessary to display the titers of IgG antibodies to the 6th strain of herpesvirus A-subtype. The technique detects viral DNA and directly the form of infection, whether it is primary infection or relapse.
- Bakposev. The cultural study of individual material aims to determine the nutrient media of the virus. The specialist determines the type of pathogen according to IgG indicators.
Treatment of herpes type 6

If the decoding of the analyzes revealed an excess of the norms for antibodies, to suppress the activity of the virus, the treatment of type 6 herpes in adults is carried out comprehensively. Let's say right away that it is impossible to completely remove HSV from the body, because it lives in nerve axons and is periodically activated under suitable conditions. Therefore, the task of therapy is to strengthen the immune system and improve the overall health of the body so that viral agents cannot multiply uncontrollably and worsen the quality of human life.
Herpes (Herpes) - translated from Greek as "a creeping, prone to spread skin disease." The disease is caused by the Herpesvirales virus, it is characterized by skin blisters all over the body and mucous membranes. Types of herpes depend on its location and pathogen, there are about 200 varieties in total, but a person is subject to only 8 of them. Each type has its own signs and causes. Types 7 and 8 of herpes are still not fully understood.
Herpes type 1
HHV 3 transmission routes:
- through common items;
- when talking, coughing, sneezing, yawning, kissing (even a friendly one).
How chickenpox manifests itself (symptoms):
- unbearably itchy skin;
- the temperature rises;
- vesicles throughout the body.
The rash spreads over the skin where the affected nerves are located. The duration of the disease is about 14 days. A person who once had chickenpox becomes a carrier of the virus for life.
- along the nerve processes, a person feels itching, burning and severe pain;
- the general body temperature rises and weakness appears;
- the affected areas are inflamed for 3 days;
- on the 2-3rd day, a group of bubbles form at the same place.

Important! The duration of the illness is approximately 2 weeks. One of the consequences of shingles is inflammation. ganglion or several nodes (inflammation of the ganglia).
Treatment of patients with chicken pox or shingles is carried out either in the inpatient department or at home. Therapy is based on the intake and use of antiviral drugs, immunostimulants, vitamins. With chickenpox, vesicles are lubricated with brilliant green or Fukortsin.
Herpes 4 types
Epstein Barr virus and Human herpes virus type 4 (EBV or EBV). Herpetic infection is the source of mononucleosis. The infection affects the nasopharynx, lymph nodes, spleen and liver. Formations can lead to cancerous formations. The consequences of the transferred Epstein Barr virus are also otitis media, sinusitis, damage to the heart muscles, inflammation of the liver and brain.
Ways of infection:
- airborne;
- domestic;
- sexual contact (including oral caresses).
The maximum amount of the virus is released during breathing and coughing. Teenagers and young adults are most susceptible to this disease.
The duration of the period from the entry of the virus into the body for its first symptoms is from 5 days to 7 weeks.

Symptoms of mononucleosis:
- hyperthermia (increased body temperature);
- swelling, inflammation and pain in the nasopharynx and;
- pain in muscles and joints;
- tonsils covered with white coating;
- the formation of vesicles on the skin and mucous membranes;
- the level of lymphocytes in the blood increases.
Diagnosis of Human herpes virus type 4 is carried out using PCR. At positive analysis, the patient is observed by 3 specialists (immunologist, infectious disease specialist and ENT).
The disease is able to go away on its own, but it is better not to wait for this moment, as complications may arise and the necessary course of treatment can be completed. Therapy of mononucleosis with mild and moderate forms is carried out at home, but the patient is isolated from others. If the case is severe, then hospitalization will be required.
There is no specific treatment regimen for type 4 herpes. Therapy is aimed at eliminating the symptoms.
Herpes type 5
Herpesvirus 5 strain (Human herpesvirus 5, cytomegalovirus, HCMV-5) is characterized by a latent form. Symptoms are more pronounced when the immune system is weakened. Men may not be aware that they are carriers of HCMV-5 for a long time. The disease affects the liver, spleen, pancreas, central nervous system and eyes.
How infection occurs and how it is transmitted:
- at breastfeeding(GW);
- in the womb;
- with blood;
- with saliva (kiss);
- during sexual intercourse.
The period of time from the entry of the pathogen into the body until the manifestation of primary symptoms is 60 days.

Signs of herpes type 5:
- elevated temperature;
- headaches, pain in the joints and in the larynx.
Important! Despite significant soreness, the tonsils and lymph nodes do not succumb to inflammation.
The real danger of the disease is for HIV-infected people, as well as those who have undergone organ transplantation, cancer patients and those taking cytotoxic drugs.
Cytomegalovirus also has negative consequences for pregnant women. Expectant mothers can give birth to a child with congenital pathologies (dysfunction of the brain, hearing, vision, breathing and digestion, skin problems and retarded development). Possibly a stillbirth.
To identify or exclude the presence of cytomegalovirus in a pregnant woman, it is necessary to do an ultrasound of the blood flow in the vessels of the umbilical cord and uterus, determine a pathologically small amount of amniotic fluid, measure heart rate, detect fetal developmental delays and abnormal development of internal organs. It is also important to pass laboratory methods research (PCR, serological diagnostics).
The goal of treatment is to eliminate the symptoms of the disease, increase and correct immunity.

Herpes type 6
Herpesvirus 6 strain (HHV-6, HHV-6) is a DNA-containing virus.
There are 2 subtypes of HHV-6:
- Subtype "A" (VGCh-6A). People with immunodeficiency are more susceptible to it. In adults, it leads to multiple sclerosis (a chronic autoimmune disease), chronic fatigue, nervous system dysfunction, and viral progression.
- Subtype "B" (VGCh-6B). Children are often exposed to this subtype. The disease progresses to roseola infantum (the sixth disease, pseudorubella).
Important! In the absence of proper treatment of both subtypes, disability and isolation from society are inevitable.
Signs and symptoms:
- small rashes (which is unusual for other types, the rash is not necessarily accompanied by itching, but the disease can also occur in an atypical form);
- hyperthermia;
- lack of appetite;
- apathy, depression;
- irritability;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- change in gait (unstability, lack of coordination, unsteadiness);
- diarrhea or constipation;
- dysfunction of the organs of vision;
- problems with speaking;
- sudden changes in mood;
- distraction;
- impaired perception and changes in sensitivity;
- convulsions.

If at least once, then the virus remains for life in a latent form and does not manifest itself. Relapses are possible with a noticeable decrease in immunity, but without the manifestation of external signs.
How HHV-6 is transmitted:
- most often infection occurs through saliva;
- sometimes the source of transmission is the palatine tonsils (airborne);
- with breastfeeding and in utero (the possibility is practically excluded);
- even less chance of infection during medical intervention.
In order to diagnose diseases, in addition to the usual examination of a doctor and questions, it is important to undergo an examination. To do this, it is necessary to take a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test, undergo serodiagnosis and a virus test.
It is impossible to get rid of herpesvirus 6 strain, the goal of therapy is to combat its manifestation. To do this, drugs with different pharmacological action(corticosteroids, antioxidants, angioprotectors, antiherpetic drugs, antipyretics, immunostimulants).

Herpes type 7
Herpesvirus type 7 (HHV-7, HHV-7) - often occurs in parallel with the virus strain 6, moreover, they are very similar to each other. The virus infects T-lymphocytes and monocytes, which leads to CFS and the development cancer lymphoid tissues.
How is it transmitted:
- the main source is airborne (since the localization of HHV-7 is saliva);
- rarely occurs infection through the blood.
The main differences between HHV-7 and HHV-6:
- strain 7 virus is not transmitted in utero;
- HHV-7 affects children at least one year old, and HHV-6 can make itself felt as early as 7 months after birth.

Symptoms:
- temporary increase in temperature without rashes;
- involuntary, paroxysmal muscle contraction;
- inflammation of the brain and its membranes;
- mononucleosis syndrome;
- sudden exanthema or roseola infantum.
To identify the herpes virus type 7 in the body, it is necessary to undergo PCR diagnostics, ELISA, a test for the virus and make an immunogram.
Medical care is to deal with the symptoms that have manifested. To date, there are no specific drugs for the treatment of HHV-7.
Herpes type 8
Herpesvirus 8 strain (HHV-8, HHV-8, KSHV) - the last abbreviation is not a typo or an accident. These letters appeared from English literature, since there the disease is called Kaposhi Sarkoma Herpes Virus. The virus infects T- and B-lymphocytes, refers to DNA-containing viruses.
Virus 8 strain is transmitted in different ways:
- sex with an infected person;
- kiss;
- blood (transplantation (engraftment) of organs or tissue sections, drug addicts are often infected when using one syringe);
- a small percentage is given to infection in utero.

Important! The risk group includes people who have undergone organ transplantation, radiation, homosexuals and drug addicts.
For an infected person with normal immunity, HHV-8 is not dangerous and does not manifest itself in any way. He is able to “uncover” his negative sides with a decrease in the body's defenses. HHV-8 provokes the appearance and development of Kaposi's Sarcoma, primary lymphoma and Castleman's disease.
Depending on what disease the patient has. There are also symptoms.
- Kaposi's sarcoma. The localization site is concentrated on the skin, lymph nodes, mucous membranes and internal organs. There are 4 types of the disease (classic, endemic, immunosuppressive, epidemic), each of them has its own characteristics.
- primary lymphoma. Oncological disease that affects the central nervous system, serous membranes.
- Multifocal Castellamne disease (MBD, angiofollicular lymph node hyperplasia, multifocal lymph node hyperplasia, angiofollicular lymphoma). A rare type of cancer that is activated against the background of HIV infection. The virus infects the lungs, lymph nodes in the mesentery and subclavian lymph nodes.

As with other agents of herpes infection, there is also no specific treatment for HHV-8. Usually prescribed drug therapy with chemotherapy, radiation, cosmetic procedures (phototherapy), in rare cases - surgery.
Only an experienced specialist can correctly determine the type of viral disease, its etiology and prescribe treatment. Although a drug against herpes infection has not yet been created, the pathology requires special attention. Timely detection of the virus in the body will help save a person from unpleasant symptoms and consequences.
Herpes virus type 6, also called HHV-6 in science, is an infection that is no less common in the world than herpes viruses of types 1 and 2, which are familiar to many. The HHV-6 virus has infected people in all countries of the world, and scientists to date have not found a single human population in which at least one infected person was not present.
The reason for this prevalence of infection lies in its specific nature ...
Key features of the virus
The HHV-6 virus is one of nine herpesviruses for which humans are either the sole or primary carrier. Simply put, it is not normal for these nine types of viruses to infect animals.
Further, like most other herpesviruses, type 6 herpes lives unnoticed in most of its hosts: having manifested itself once, it forces the immune system to develop such protection that will further suppress the development of infection throughout a person's life. Moreover, human immunity reacts more strongly to the herpes virus type 6 than to the type 1 virus, which usually causes the well-known “cold” on the lips. Because of this, even after past illnesses, stress and a seasonal decrease in immunity, the recurrence of type 6 herpes is almost always asymptomatic.
As a result, most people who carry HHV-6 are not even aware of its presence in the body. Like other human herpesviruses, it is indestructible: today medicine has no medicine capable of completely destroying this virus in the body.
And, perhaps, most importantly, the sixth type of herpesvirus most often and pronouncedly manifests itself in children. Today, scientists believe that this infection is most often transmitted through saliva, and therefore young children catch this disease almost from the very first days of contact with their mother or other people who are carriers of the virus.
However, in the first few months of life, infection of the child does not lead to any consequences: the innate immunity transmitted from the mother confidently suppresses viral particles. Only in the event that the mother's body is not familiar with this infection, and the child becomes infected from another person, typical symptoms of the disease can occur in an infant already in the first months of his life. Children usually get sick between the ages of 4 and 13 months.
The herpes virus type 6 can mask its manifestations under the symptoms of other diseases. Often in medical practice there is an error in which the presence of a pathogen in the body is determined by the presence in the blood of immunoglobulins that are common or very similar to those for the herpes virus type 7. Due to this cross-reaction and some other reasons, misdiagnosis is often made, and the actual statistics of type 6 herpes are very inaccurate.
Transfer Methods
In the vast majority of cases, the HHV-6 virus is transmitted through saliva, in which it is found in 90% of adults. Much less often, the palatine tonsils act as a reservoir for infection. In any case, the possibility of transmission of the virus from mother to child during breastfeeding is practically excluded.
In some cases, doctors register the transmission of the pathogen from mother to child directly during childbirth. As a result of the studies, it turned out that in 2% of women in labor, the herpes virus is present in the vaginal secretion, and in another 1% - in the blood in the umbilical cord. It is not surprising that during childbirth, the infection can easily enter the child's body through microtraumas and scratches.
Most often, type 6 herpes affects children aged 7-12 months, and in general, 90% of primary infections occur in children under the age of 2 years. In infants up to 4 months, the titer of IgG antibodies obtained from the mother and causing immunity against herpes is still quite high. With a decrease in IgG levels at a later age, the risk of the disease increases sharply.
Discovery history
The herpes virus type 6 was discovered and sufficiently studied in 1986 by American biochemists Daram Ablashi and Robert Galo. They were engaged in the study of cultured blood cells in patients with AIDS and various lymphoproliferative diseases. In the cells of one of the cultures, they found intraplasmic bodies, which were originally named B-lymphotrophic virus.
Soon after more thorough research by Dr. Alabashi, it turned out that the virus belongs to the herpes viruses. It was named HHV-6, and already in 1988 a connection was established between it and sudden exanthema (another name is roseola). The virus itself is the etiological agent of this disease, while earlier scientists believed that roseola was caused by an enterovirus unknown before. After careful research, HHV-6 was divided into two subtypes, which in 2012 were decided to be classified as separate species. Of these, HHV-6A causes various disorders in the nervous system of adults, and HHV-6B leads to childhood roseola.
The most obvious symptoms of the disease are when children are infected with the HHV-6B virus. It is they who are most often referred to when describing type 6 herpes.
Symptoms of the disease caused by the herpes virus type 6
The main symptom of the disease caused by the sixth type of herpes virus is extensive small rashes on the skin of a child, which is often referred to as infantile roseola, sixth disease or pseudorubella. Small rashes spread all over the child's body, slightly raised above the skin and usually do not cause itching.
Always a few days before the appearance of rashes, the child has an increase in temperature, characteristic of fever. However, even at this body temperature, the child remains active. The high temperature lasts for 4-5 days, after which it drops sharply and sprinkles the child.
It happens that the disease proceeds without rashes, and such an exacerbation is easily confused with enterovirus infection or measles. According to studies, in 20% of cases of diagnosis of fever, the real cause is herpes. The list of such applicants, under which the disease can disguise itself, is long: measles, rubella, meningitis, otitis, sepsis, drug rash, bacterial pneumonia, infectious erythema.
If the child has rashes, then they do not stay on the skin for long: in some cases they disappear after a few hours, sometimes they can persist for several days. In parallel with them, the child loses his appetite, he becomes inactive and irritable, sometimes he has an increase in lymph nodes.
More serious manifestations of primary infection with herpes type 6 are:
- meningoencephalitis;
- myocarditis;
- fulminant hepatitis;
- thrombocytopenic purpura;
- mononucleosis-like syndrome;
- various pneumonias.
It is important to remember that the disease often manifests itself as a companion of other diseases, and many of its manifestations can be easily mistaken for symptoms of such etiological precursors.
Sometimes, against the background of herpes, eosinophilia and hypersensitivity syndrome to various medications can develop.
After childhood illness caused by the HHV-6 virus, the body develops lifelong immunity, and in adults the infection does not manifest itself in any way. Despite the fact that the virus is often activated in the body, when a blood test can determine its presence, in people with normal immunity, such relapses occur asymptomatically.
In those rare cases when the virus enters an adult for the first time, it causes about the same symptoms as in children: fever and skin rashes. It is noteworthy that in many cases such symptoms are confused with side effects from taking various antibiotics.
The prognosis for a disease caused by the herpes virus type 6 is always positive: there have been no recorded cases of death from it in patients. However, the very presence of an infection in the body and its imperceptible activity often leads to the development of other, more dangerous and sometimes fatal diseases ...
Possible Complications
In children, febrile convulsions may occur at the stage of fever, and in very rare cases pneumonia, meningitis or encephalitis develop. The consequence of convulsions in very early age may develop epilepsy.
In adults, complications from a recurrence of type 6 herpes usually occur when immunity is reduced after past illnesses or with a seasonal lack of vitamins in the diet, or with intentional suppression of immunity, which is required by some methods of treating cancer and blood diseases. And these complications are often extremely dangerous.
The participation of the herpes virus HHV-6 in the development of the following diseases has been proven:
- multiple sclerosis - autoimmune disease nervous system, characterized by disturbances in the nervous system and the appearance of various symptoms of neurosis. This disease has nothing to do with senile memory loss, although a disorder of mental functions may be one of its consequences;
- Pink lichen is not the most terrible disease, which, nevertheless, brings discomfort and itching when spots appear on the skin. Pink lichen is not treated, but goes away on its own, and the manifestations of its symptoms can be reduced with the help of special medications;
- Chronic fatigue syndrome is one of the most common diseases associated with herpes type 6. It is characterized by disorders in the central and peripheral nervous systems, metabolic disorders and feeling constant fatigue. Chronic fatigue syndrome starts like a common cold or infectious disease, leads to an increase in temperature for several days, and then to an apparent recovery. However, weakness and lack of energy in the patient persist even after the disappearance of other symptoms, which can lead to mental disorders and social problems. Despite the fact that the leading role of the HHV-6 virus in causing chronic fatigue syndrome has not been proven, in almost all cases of the development of this disease, recurrent herpes virus particles type 6 are found in the patient's body;
- Autoimmune thyroiditis is a chronic inflammation thyroid gland, with insufficiently intensive treatment, often developing into hypothyroidism;
- Retrobulbar neuritis. Medicine knows three cases of the development of this disease due to the recurrence of herpesvirus type 6, and all three developed in infants. This disease is extremely dangerous in that it leads to loss of vision in a short time;
- Liver failure, sometimes reported as a consequence of the manifestation of HHV-6 in young children;
- Crayfish. All herpesviruses tend to cause oncology to some extent, and HHV-6 is no exception. Most often, it leads to the development of Kaposi's sarcoma, lymphomas, leukemia, cervical cancer and brain tumors. Of all the consequences, these are the most dangerous and at the same time quite often manifest themselves.
Today, doctors and researchers cannot unequivocally state whether these diseases are caused by the reactivated herpes virus type 6, or whether they appear in parallel due to a weakened immune system. However, cases when any of these diseases appears after a recurrence of herpes are more frequent than cases when the virus continued to be in the body in a latent form during a developing disease. Therefore, most likely, it is the herpesvirus that in many cases is the cause of the development of these diseases.
Methods for diagnosing diseases
Theoretically, the diagnosis of childhood roseola should not cause any difficulties due to the large number of very characteristic symptoms. However, in in large numbers cases of infection caused by the HHV-6B virus are confused with rubella, and sometimes with other childhood diseases. Therefore, confirmation of the diagnosis is often required using serological methods, polymerase chain reaction, immunohistochemical and virological methods.
In newborns, class G immunoglobulins received from the mother are responsible for immunity against herpes infections. Their presence in the blood can be detected as early as 7-10 days after birth, and it reaches a maximum at 2-3 weeks. To accurately confirm the presence of the herpes virus type 6 in the body, a double blood test is required. In cases where IgG titer increases by 4 times or the result goes from negative to positive, we can talk about infection with a virus.
Later, class M immunoglobulins will be responsible for the immune response. They begin to be produced in the body 3-4 days after the onset of the disease, and already at this time their titer can be determined to diagnose the disease. But there are several difficulties here: with a relapse of the disease, the corresponding class M immunoglobulins do not appear, and in some children their number during a primary infection is so small that it is impossible to determine the titer by conventional methods.
For the diagnosis of herpesvirus type 6, a culture method using peripheral blood or saliva mononuclear cells has proven itself well. The main advantage of this method is the ability to detect the disease in the fertile phase before the appearance of a red rash or at any time during the life of the carrier of the virus, even in the latent phase. However, this method is sometimes not available, and in people with immunodeficiency may give incorrect results.
Using the polymerase chain reaction, specialists can estimate the amount of viruses in various body fluids (most often in the blood), and with a high degree of probability predict the possibility of its recurrence in the future.
Interestingly, today in adults it is possible to determine the type A or B of herpes HHV-6. This is done using the method of monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies.
Methods of treatment
All methods of treating diseases caused by type 6 herpesvirus are only a fight against its manifestations (the so-called symptomatic treatment). Medicine still does not have the means to completely rid the body of this virus. And the fight against a primary infection can be considered meaningless at all - it is wiser to give the body the opportunity to develop immunity for life.
When symptoms of the disease appear, a typical set of drugs is usually used to combat herpes viruses.
In case you get sick Small child, it first of all needs to be shown to the doctor. True, doctors can not always distinguish roseola from rubella, but be that as it may, the doctor will prescribe a set of drugs in accordance with the individual characteristics of the baby.
Most often, the drug complex includes:
- Ganciclovir, most effective against HHV-6B;
- Cidofovir;
- Foscarnet, which performs equally well against both types of HHV-6.
At the same time, Ganciclovir and Foscarnet are allowed for use by children from the age of 12, but in the West, in cases of complicated infections, Ganciclovir is used more often.
Acyclovir, which is very common today against herpes type 6, demonstrates very low efficiency.
In parallel, in different countries of the world, the possibilities of using drugs such as Lobucavir, Cidofovir, Adefovir in the treatment of type 6 herpes are being studied, but there are no clear results on their testing yet. Nor have even experimental versions of vaccines against the HHV-6 virus been developed.
Antipyretics based on paracetamol and ibuprofen are used as medications to relieve symptoms. Most often, children are prescribed Panadol and Nurofen. With an increase in the temperature of the child, you should often and plentifully drink water, compotes and herbal teas.
A big plus of roseola is the absence of itching in places of redness. The child does not worry and does not scratch these rashes, and therefore, there is no need to worry that he will bring any additional infection under the skin.
Throughout the entire period of illness, the child should be given vitamin preparations containing vitamins A, E and C. You should consult a doctor about which particular drug to give in each individual case.
In adults, the same symptoms as in children can appear during organ transplants, when the immune system is suppressed so that new tissues are not rejected. At the same time, it is rather difficult to treat herpes at this moment due to the need to support low immune status sick.
Although rather unpleasant, but an obvious fact is the poor attention of medical specialists to the study of the characteristics of the course of type 6 herpes in patients in Russia. For all the time that science has been familiar with this infection in our country, isolated studies have been carried out, of which the examination of children in the nursery was quite large-scale. infectious diseases hospital Petersburg from April to September 2007. Then a total of 52 patients with pronounced roseola were identified. Of these, the presence of the virus was confirmed in 31 by laboratory data of serological analysis, and 15 patients did not come to donate blood for the detection of IgG antibodies.
In general, in our country, the diagnosis of rubella or an allergic rash is the norm in the presence of obvious roseola in children. At the same time, not only are undesirable and rather dangerous antibiotics prescribed to patients, but complications after roseola, such as meningitis or hepatitis, often occur quite often. In many cases, this state of affairs is due to the fact that the description and treatment of roseola is not described in professional guidelines for infectious diseases.
Doctors noted that taking drugs based on interferon helps to reduce the risk of recurrence of type 6 herpes infection. However, just for the sake of preventing the reactivation of the virus, you should not drink drugs with interferon. It is much more reasonable to carry out a comprehensive prevention of exacerbation of herpes.
Prevention of recurrence of the disease
The main key to reducing the frequency of relapses of herpesvirus diseases and reducing the risk of complications is the support of a healthy immune system. To do this, it is necessary to perform a fairly well-known set of measures:
- maintain a high level of physical activity and exercise regularly;
- ensure the presence of fresh fruits, berries and vegetables in the diet, increasing this amount during the season for the development of colds;
- once again not to expose yourself to the risk of infection with various infectious diseases;
- have a good rest and observe the optimal work and sleep schedule for the body;
- often be in the fresh air, harden.
Vitamin preparations are no less useful for the body, especially in the season of lack of vitamins in the diet. To maintain immunity, you should pay attention to the popular vitamin-mineral complexes.
For young children, it is especially important to get enough breast milk. And although specific antibodies against herpesviruses do not get into milk, all other immunocompetent substances are contained in it, which will help the baby, in case of illness, easily and without consequences to transfer it.
Useful video: doctor's comments about baby roseola (sudden exanthema)
Herpetic infection is one of the most "many-faced" diseases. In total, doctors distinguish over a hundred different types of herpes pathogens. About 8-9 species are found in humans, they can be called relatively studied. They differ in external manifestations, the degree of threat to human health, the nature of the course of the disease, but all are considered equally contagious. According to some reports, from 80 to 96% of the world's inhabitants are infected with the herpes virus type 6. He is one of the most dangerous representatives of his class.
Type features
The sixth type of herpes virus was discovered relatively recently (in the mid-80s of the twentieth century). It is a DNA-containing viral agent that infects T-lymphocytes (responsible for immune response). His study continues to this day. Within HHV type 6, two subspecies of pathogens can be distinguished:
- 6A (HHV-6). It is more typical for adults. The virus negatively affects the work of the central nervous system, presumably, the development of sclerosis is associated with its presence in the body;
- 6B (HHV-6-B). The variety is most often diagnosed in younger patients.
Herpes type 6 is classified as an incurable disease. Antivirals allow to reduce the activity of the pathogen and achieve remission, but it is impossible to completely cure a herpes infection at the current level of medicine.
Often, primary immunity to the disease is innate (if the mother has antibodies to this type of herpes). Therefore, for the first six months of life, such babies are protected from infection, they are extremely rarely diagnosed with type 6 herpes (children from 7 months to a year are in the main risk group). Infection, as a rule, occurs during the first 3 years of life, after which specific immunity develops, which makes it possible to endure re-infection almost asymptomatically.
The virus remains in the human body for latent form. It begins to actively multiply and have a devastating effect on health only during periods of a significant decrease in immunity.
In most cases, the herpesvirus type 6 is diagnosed in patients with HIV (during immunodeficiency studies, it was discovered for the first time). 
A feature of the virus is that the external signs of infection often mimic completely different diseases (colds, allergic rashes, measles or rubella). This complicates the diagnosis.
Ways of infection
Viral agents are found in saliva, vaginal secretions, blood, cerebrospinal fluid, and sputum. Known methods of infection:
- by airborne droplets;
- vertical transmission to the child from the mother during labor;
- contact method of infection (including the possibility of infection through kissing and sexual contact);
- during medical manipulations - during blood transfusion and during operations.
The latest research has proven the possibility of transmission of the virus, integrated into the DNA of the parents, already at the time of conception. 
Primary infection usually occurs during childhood. The younger the child, the harder the infection is tolerated. At the same time, a stable immunity is formed, which suppresses the development and external manifestations of the disease throughout a person’s life.
Carriers of the virus are usually unaware of its presence in the body. Even in the absence of pronounced symptoms, the disease can be transmitted from them to healthy people.
Signs of defeat
Outward symptoms are age features. After the incubation period (1-2 weeks after the virus enters the body), the child has the following symptoms:
- a rapid rise in temperature, sometimes up to 40 o, which is difficult to bring down;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- fever, lethargy, loss of appetite;
- rarely - convulsions, rolling eyes;
- sometimes - redness of the throat, rhinitis.
 The fever persists for 3 days, then the above symptoms disappear, but instead a rash appears (roseola, sudden exanthema). However, infection in almost half of cases (about 40%) is not accompanied by skin rashes.
The fever persists for 3 days, then the above symptoms disappear, but instead a rash appears (roseola, sudden exanthema). However, infection in almost half of cases (about 40%) is not accompanied by skin rashes.
Primary infection with type 6 herpesvirus in adults is extremely rare. When this happens, the symptoms are similar to those of children, but manifest to a lesser extent - fever, lethargy, swollen lymph nodes.
More often, signs of pathology in adulthood are noticeable with a relapse of infection, provoked by a decrease in immunity. They are usually mistaken for a cold or flu:
- high temperature, fever;
- intoxication;
- joint pain;
- rhinitis, discomfort in the throat.
Activation of the virus provokes changes in mental state. Appears chronic fatigue for no apparent reason, apathy, in some - irritability and aggressive behavior.
 Sometimes the 6th type of herpes infection is mistakenly called HSV. This is not true, since only types 1 and 2 are classified as HSV - herpes simplex viruses ( feature- the appearance of itchy blisters on the lips and genitals). The sixth type, provocative in childhood roseola, and in adults serious pathologies of various organs, does not belong to this group.
Sometimes the 6th type of herpes infection is mistakenly called HSV. This is not true, since only types 1 and 2 are classified as HSV - herpes simplex viruses ( feature- the appearance of itchy blisters on the lips and genitals). The sixth type, provocative in childhood roseola, and in adults serious pathologies of various organs, does not belong to this group.
The danger of HHV 6 and possible consequences
The virus becomes a threat to health and even life when there is a pronounced decrease in immunity. This happens in the following cases:
- the presence of severe chronic diseases who have not been treated for a long time;
- lack of vitamins;
- prolonged and severe overwork, stress;
- hormone therapy;
- radioactive exposure, the development of radiation sickness;
- cancer treatment - chemotherapy;
- immunodeficiency, AIDS.
- prevention of rejection of transplanted organs with the help of immunosuppressants.
The “awakened” virus begins to have a devastating effect, affecting various systems and organs. Often this manifests itself in the form of diseases of the blood, liver, central nervous system, lymph nodes, kidneys and salivary glands. With a high degree of probability, a connection has been established between the 6th type of herpes and the development of the following pathologies:

If a woman planning a pregnancy has a primary infection with HHV (human herpesvirus), then conception should be postponed until the formation of specific immunity (the appearance of antibodies in the blood). Otherwise, the risk of miscarriage increases.
During the period of remission, the type 6 virus does not pose a threat, but against the background of a decrease in immunity, the infection worsens, which is extremely dangerous. It contributes to the development of serious diseases, up to death.
Diagnosis and treatment
Herpes infection type 6 is one of the most difficult to diagnose pathologies in people of any age. The reason lies in the similarity of external signs of infection with other common diseases. 
Recognize HHV type 6 in adults is possible only with the help of special tests. For this purpose, the following types of studies are usually used:
- polymerase chain reaction (PCR). This method finds viral DNA;
- ELISA - enzyme immunoassay. Finds out the DNA of the viral agent, determines whether the disease is a relapse or primary infection;
- special virological studies (for example, the cultivation of the pathogen).
The effectiveness and accuracy of diagnosis largely depends on the state of immunity, the stage of the disease, and a number of other factors. In some cases, a positive test result may be false.
A feature of type 6 infection is its low sensitivity to drugs.
 In cases where an exacerbation of the virus needs to be treated, adults may be recommended special antiviral chemotherapy, or complex drug tactics using:
In cases where an exacerbation of the virus needs to be treated, adults may be recommended special antiviral chemotherapy, or complex drug tactics using:
- antiviral agents (Ganciclovir, Foscarnet, Cidofovir);
- immunomodulators (Kipferon, Derinat, Viferon);
- antipyretic drugs (Ibuprofen, Paracetamol);
- vitamin and mineral complexes (Supradin, Alphabet, Complivit).
Treatment folk remedies in the case of a severe course of the disease, it will hardly be effective, but sometimes they still resort to it. ethnoscience offers to fight the virus using medicinal plants:
- celandine;
- horseradish;
- dogwood;
- liquorice root;
- black poplar.
 They are credited with antiviral properties and the ability to increase immunity.
They are credited with antiviral properties and the ability to increase immunity.
It is impossible to destroy pathogenic microorganisms; all therapeutic measures are aimed at reducing acute stage and bringing the infection into remission.
Prevention
It is almost impossible to avoid infection with herpes type 6. That's why preventive measures are mainly aimed at keeping the virus in a dormant state. There is a standard set of actions necessary to maintain health and maintain immunity at a high level:
- quitting smoking and alcohol;
- adherence to the correct daily routine;
- complete rest;
- balanced diet;
- timely diagnosis and treatment of various diseases, including infectious ones;
- physical activity;
- adequate exposure to fresh air.
All this in combination allows you to maintain a state of remission and protect the body from the harmful effects of HHF agents.
Despite the proven association of the virus with a group of extremely dangerous diseases, its presence in the body does not affect the quality and duration of life if the immune system is functioning normally.
Therefore, even if an infection is diagnosed in a person, this is not a sentence. It is enough to monitor your health and prevent a decrease in immunity.