For a normal metabolism and energy in the body, it needs a constant supply of substrates from the outside, that is, with food, water and air. Their most important components are organic compounds, vitamins and mineral components - potassium, magnesium, sodium, copper, iron and many others. The last of these is part of the erythrocytes, the only oxygen carrier cells in our blood, and therefore the exchange of iron is so important for the body. And with its violations, one way or another, an icteric syndrome develops, characterized by the fact that total bilirubin is elevated. Now let's look at all the important points.
This change is hereditary and is usually asymptomatic, although jaundice may appear under conditions of excessive stress, stress, fasting, previous infections, or after taking certain medications, as the concentration of bilirubin in the blood increases in these situations.
Fatigue is another symptom that may indicate the presence of the syndrome. The disadvantage of this disease is that it is asymptomatic and sometimes goes unnoticed until jaundice appears. In these cases, the specialist may conclude that the patient has an increased production of indirect bilirubin and a diagnosis of Gilbert's syndrome.
iron exchange
A person receives iron exclusively from food. Its highest concentration is observed in the liver of animals, some nuts (pistachios, peanuts, pine nuts, cashews), legumes (lentils, peas), cereals (buckwheat, wheat, oats, barley), spinach, corn. At the same time, its required amount for the heme, which is the basis of the erythrocyte, is first replenished, and only then iron is deposited in its depot in our body, which is about 3-4 grams, it is ions associated mainly with plasma proteins and enzymes (ferritin, transferrin, xanthine oxidase, ferroflavoproteins, succinate and NADH dehydrogenase, and others). But this happens normally, now let's look at his losses and some pathological conditions.
It is usually diagnosed in adolescence and adolescence. The aesthetic aspect and the fear of suffering from some important liver related disease are the main reasons for consultation for this syndrome. People with this syndrome often experience fatigue.
There is no condition for this preventive measures because it appears for reasons, almost always, outside the patient. If there is a possibility that a family member has been hurt or injured, the patient will usually be advised and thus know that the jaundice is not serious.
In these cases, it is also recommended to avoid situations of stress and excessive stress. Currently, there is no difference in the types of this syndrome. To determine if a patient is suffering from this syndrome, a specialist will perform a blood bilirubin test. In most cases, the result is a slightly elevated total bilirubin level, with most being indirect bilirubin. More specifically, the total level of this substance does not exceed 2 milligrams per deciliter.
Causes of Loss of Important Minerals
Some of the physiological processes in which iron loss occurs are menstruation and pregnancy in women. However, perhaps the most significant situations are blood loss, intoxication, anemia of various origins, serious illnesses internal organs, malignant neoplasms. If the loss was insignificant, then it manages to be replenished in a short time, and at the same time the patient has no symptoms of its deficiency. However, there are also those diseases in which the volume of iron is preserved, but its metabolism is sharply disturbed. Such cases include icteric syndrome of any origin, since it reveals an increase in the main metabolite - bilirubin. To begin with, we will try to analyze its metabolism in the body and the causes of increased bilirubin in the blood: this is important for understanding the pathogenesis of these diseases.
Choosing the Right Diet
This condition is associated with a genetic problem, but no genetic testing is required to establish a diagnosis. Gilbert's syndrome is a benign disease, so no treatment is required. Behind the skin, the liver is the largest vital organ in the body. It performs over 500 chemical processes, produces 160 different proteins, coagulates the blood, stores and converts sugar into glycogen, metabolizes, detoxifies, and synthesizes numerous nutrients.
A blood test checks the values of various liver enzymes to make sure it is working properly or if you have any injury or illness. The most frequently analyzed enzymes. Values considered normal or reference are not published as they may vary from laboratory to laboratory.
Hemoglobin exchange: the first phase
 Bilirubin is one of the most important pigments that make up bile and is excreted from the body precisely at its expense. It travels a long way through the vessels, yet it performs important transformations in hepatocytes and, finally, is secreted into the intestine for excretion into the environment with feces. So, this substance is formed during the breakdown of red blood cells and is immediately captured by carrier proteins for transport to the main laboratory - the liver. Such a fraction is called indirect or unbound, because bilirubin in it is in unchanged form. This happens because in its free form it easily penetrates the membranes of any cells and has a pronounced toxic effect primarily on neurons. Thus, its capture is a normal defensive reaction.
Bilirubin is one of the most important pigments that make up bile and is excreted from the body precisely at its expense. It travels a long way through the vessels, yet it performs important transformations in hepatocytes and, finally, is secreted into the intestine for excretion into the environment with feces. So, this substance is formed during the breakdown of red blood cells and is immediately captured by carrier proteins for transport to the main laboratory - the liver. Such a fraction is called indirect or unbound, because bilirubin in it is in unchanged form. This happens because in its free form it easily penetrates the membranes of any cells and has a pronounced toxic effect primarily on neurons. Thus, its capture is a normal defensive reaction.
Signs of subhepatic jaundice
Some liver values may go down or up, but only your doctor can tell you if this is normal or not. This enzyme allows you to detect liver damage and the appearance of diseases in the long term. It is found mainly in hepatocytes. It is released when cells are damaged or destroyed.
What stains bilirubin
This is not considered to be very specific to the liver, as reference values depend on many other factors. Active levels of this enzyme may indicate active hepatitis or other causes such as viruses, obstruction bile ducts, excessive consumption of alcohol, the harmful effects of drugs or toxins. This enzyme is also affected by low blood pressure.
Phases of neutralization and release of bilirubin
However, these proteins cannot accompany it all the way to the intestines, because the body still needs them for many other functions, and therefore bilirubin must be subjected to such transformations that it loses its ability to pass into cells. For this, in hepatocytes (structural cells of the liver parenchyma), it is conjugated, that is, it is bound by glucuronic acid, which, simply put, makes it heavier. Thus, under the action of the enzyme UDP-glucuronyltransferase, bilirubin-diglucuronide is formed. Further, from hepatocytes, it enters the bile and, in its composition, is excreted into the intestine during digestion. Now, going along with the food bolus, first into the small and then into the large intestine, under the influence of the bacterial flora, it is released again and turns into urobilinogen, then into urobilin and stercobilin, which are directly excreted with feces. However, always an extremely small amount of bilirubin returns to the portal vein and is carried to the kidneys, from where it is removed in the urine.
Aspartate aminotransferase or aspartate phosphatase
It is used to detect liver damage or chronic liver disease. It is released when cells are damaged or destroyed. When some of these indicators show very high values, they may indicate chronic liver diseases, viral hepatitis. It can also indicate cirrhosis, intoxication, or overdose.
Features of the circulation of newborns
Another function of the liver is the production of bile, which helps us digest fats. Bile flows through the liver through a system of small ducts, is stored in the gallbladder and released into small intestine. This enzyme can also be found in the pancreas, bones, and intestines.
Limits of the norm
Violation of the metabolism of this important pigment can occur in three main stages: circulation in the blood during the breakdown of red blood cells, capture in the liver and excretion with bile. However, with all these options, it will be detected in the blood: total bilirubin will be increased, mainly either due to its direct or indirect fraction. So, its normal plasma concentration is considered to be about 8.5-20.5 micromoles per liter. If this number increases to 85, then a state of hyperbilirubinemia occurs. mild degree, from 86 to 169 - moderate and, finally, over 170 µmol / l - severe. This is about the case, if it is simply revealed that the total bilirubin is elevated. However, the norm also exists separately for fractions: direct - up to 5.1, unbound - up to 16.5 µmol / l.
These problems can be caused by a problem in the liver, gallbladder, or the tubes that connect them. It may also indicate gallbladder dysfunction or blockage. Albumin is a protein produced by the liver and is very abundant in blood plasma. They usually also ask to monitor the functioning of the kidneys. Albumin analysis is very common. If the liver has chronic illness or acute injury, blood albumin levels will usually be low.
This laboratory test measures the total amount of bilirubin in the blood, including direct and indirect bilirubin. Bilirubin occurs during the normal process of blood cells after death, the liver releases bilirubin through bile. An excess of bilirubin in the analytical results is confirmed by the patient's skin and a white, yellowish eye known as jaundice. Through blood tests, elevated levels of bilirubin can be detected before jaundice appears. This test is also used to detect hemolytic anemia.
Prehepatic type of jaundice
So, in case of violation at the first stage, total bilirubin in the blood is increased mainly due to the indirect fraction. This is explained by the etiology of the condition, namely, the increased breakdown of red blood cells in the vascular bed. This can occur with congenital forms of hemolytic anemia (defects at the genetic level of the red blood cells themselves, their enzymes, hemoglobin) or acquired (immunological diseases with an attack on one's own red blood cells, exposure to toxins and poisons, viruses, bacteria and other microorganisms). Thus, the pathogenesis is based on the increased formation of bilirubin, due to which the liver cells simply do not have time to capture such a huge amount of it, and it accumulates in the skin and mucous membranes, and then in internal organs causing them severe damage. This is how the suprahepatic type of jaundice is formed.
Indirect bilirubin is dead red blood cells and does not dissolve in water. To eliminate it from our body, it must go to the liver. Direct bilirubin becomes the water-soluble form of bilirubin in the liver. The ratio of indirect bilirubin to direct bilirubin may change if the liver has difficulty carrying out the transformation.
Bilirubin is secreted by bile and its outlet channel, ending in the small intestine. Cholestasis, damage or obstruction of the bile ducts can lead to elevated level bilirubin. This test is needed to check the health of the liver and kidneys. The total amount of proteins and albumin is usually requested in routine medical examinations. If the protein result is changed, the doctor will ask other tests to analyze the cause in more depth.
Hepatic type of jaundice
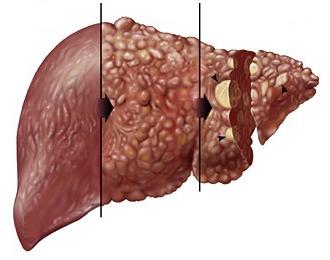 If the violation occurs at the second main stage, then hepatocytes do not have time to capture and process even the normal amount of hemoglobin metabolite entering them, and as a result, due to both fractions total bilirubin elevated. The reasons for this are severe destructive changes in the liver. These include hepatitis of various origins (toxic, alcoholic, viral) and cirrhosis. Thus, the causes of increased bilirubin in the blood lie in the fact that hepatocytes cannot work adequately, either due to inflammation in them, or due to their insufficient number. Most common cause, of course, is A-type, B, C, delta, E or PP. This is how the hepatic (parenchymal) type of icteric syndrome develops, which is accompanied by vivid symptoms of mesenchymal inflammation and hepatociliary insufficiency.
If the violation occurs at the second main stage, then hepatocytes do not have time to capture and process even the normal amount of hemoglobin metabolite entering them, and as a result, due to both fractions total bilirubin elevated. The reasons for this are severe destructive changes in the liver. These include hepatitis of various origins (toxic, alcoholic, viral) and cirrhosis. Thus, the causes of increased bilirubin in the blood lie in the fact that hepatocytes cannot work adequately, either due to inflammation in them, or due to their insufficient number. Most common cause, of course, is A-type, B, C, delta, E or PP. This is how the hepatic (parenchymal) type of icteric syndrome develops, which is accompanied by vivid symptoms of mesenchymal inflammation and hepatociliary insufficiency.
It is tested for diseases that affect the heart, liver, muscles, kidneys, lungs, and blood. Important increases in lactate dehydrogenase activity can be observed in megaloblastic anemia, untreated pernicious anemia, Hodgkin's disease, cancer abdominal cavity or lungs, shock, hypoxia.
Prothrombin time and normalized international ratio
Elevated levels of the enzyme are found in about one third of patients with kidney disease, especially those with tubular necrosis or pyelonephritis. However, these scores do not correlate well with proteinuria or other parameters of kidney disease. The time it takes for blood to clot is measured.
Subhepatic type of jaundice
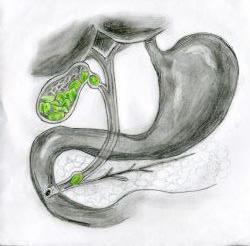 And, of course, a violation of bilirubin metabolism can also occur at the third main stage, that is, during the excretion of bile. One way or another, with this variant, its exit is blocked along the pathways either from the liver, or already from the vesicafellea. As a result of such changes, bile accumulates in the ducts and bladder, its pressure gradually increases, and as a result, it returns (this phenomenon is called regurgitation) to the intrahepatic ducts and further to blood vessels, that's why the total bilirubin is elevated. At the same time, of course, there are other changes in biochemical analyzes. So, cholemia occurs in the blood, that is, enzymes also enter it, and cholestasis is formed in the ducts themselves, that is, stagnation of the secret. Clinically, this will be expressed by jaundice of the sclera, mucous membranes and skin (yellowish color with a green tint), and in the analyzes there will be not only total and direct bilirubin increased, but also bile acids, cholesterol, triglyceride level, gamma-glutamyl transferase activity.
And, of course, a violation of bilirubin metabolism can also occur at the third main stage, that is, during the excretion of bile. One way or another, with this variant, its exit is blocked along the pathways either from the liver, or already from the vesicafellea. As a result of such changes, bile accumulates in the ducts and bladder, its pressure gradually increases, and as a result, it returns (this phenomenon is called regurgitation) to the intrahepatic ducts and further to blood vessels, that's why the total bilirubin is elevated. At the same time, of course, there are other changes in biochemical analyzes. So, cholemia occurs in the blood, that is, enzymes also enter it, and cholestasis is formed in the ducts themselves, that is, stagnation of the secret. Clinically, this will be expressed by jaundice of the sclera, mucous membranes and skin (yellowish color with a green tint), and in the analyzes there will be not only total and direct bilirubin increased, but also bile acids, cholesterol, triglyceride level, gamma-glutamyl transferase activity.
The presence of clotting factor inhibitors. Estrogen-containing drugs such as birth control pills and hormone replacement therapy.
- Anticoagulant drugs such as warfarin, heparin.
- Liver problems.
- Insufficient levels of proteins that coagulate the blood.
- Congenital deficiency factor.
Reasons for development
The etiology of obstructive or, as it is also called, subhepatic, jaundice, is quite extensive. The most common cause is blockage of the biliary tract by a stone in calculous cholecystitis or cholelithiasis, as well as helminthic invasion, when a lump of worms is localized inside the ducts or pronounced cholangitis, when they are inflamed and the lumen is obturated either due to swelling of the walls, or due to infiltration from them. And, of course, this explains the fact that direct and total bilirubin is elevated. The causes of other pathologies, in any case, are due to pressure from the outside. Most often this is observed due to the growing tumor process, usually affecting the head of the pancreas. But such a situation can also occur with biliary cirrhosis of the liver, when the ducts are compressed by growing areas and strands of connective tissue.
AT laboratory analysis only 3 parameters are measured, although usually the main one is usually indicated, which is the sum of two. But what do we do when we find elevated bilirubin, what are its causes and how can we reduce it? What is high bilirubin? This process is generated in the spleen, an organ that, among other important functions, is able to destroy various old blood cells. There are three types of bilirubin in the blood, so the reasons that caused its increase will be different. This is basically a parameter that when expressed indicates that there may be some type of liver disease, which is also known as conjugated bilirubin.
Physiological jaundice of newborns
![]() However, not all jaundices are pathological conditions of the body. So, if the total bilirubin is elevated in a child immediately at birth or a few hours after it, and the skin and mucous membranes have a bright icteric hue, then you should not immediately sound the alarm. Indeed, in newborns, this is a physiological state, called transient, since it is transient. Of course, the question arises from his worried mother, who learns that her child has elevated bilirubin: "What should I do?" The answer is simple: wait. In this case, only expectant tactics are really shown, since within a few days (usually up to three to five), jaundice gradually disappears. And only if it is delayed, the baby's condition worsens, and the total bilirubin remains elevated, the treatment is carried out urgently, namely, detoxification therapy and ultraviolet irradiation are used. Now let's look at the pathogenesis of this condition.
However, not all jaundices are pathological conditions of the body. So, if the total bilirubin is elevated in a child immediately at birth or a few hours after it, and the skin and mucous membranes have a bright icteric hue, then you should not immediately sound the alarm. Indeed, in newborns, this is a physiological state, called transient, since it is transient. Of course, the question arises from his worried mother, who learns that her child has elevated bilirubin: "What should I do?" The answer is simple: wait. In this case, only expectant tactics are really shown, since within a few days (usually up to three to five), jaundice gradually disappears. And only if it is delayed, the baby's condition worsens, and the total bilirubin remains elevated, the treatment is carried out urgently, namely, detoxification therapy and ultraviolet irradiation are used. Now let's look at the pathogenesis of this condition.
However, it can also alert you to any obstructions in your bile ducts. The main causes are: Acute hepatitis: occurs when there is inflammation in the liver, especially due to a lack of elimination of toxins that accumulate in this organ. Dubin Jochson Syndrome: A genetic background in which the liver tends to change color as a result of the accumulation of pigments. Bile duct obstruction: This is another cause and is not as closely related to the liver. Causes of elevated bilirubin Causes of high indirect bilirubin In this case, we are faced with a parameter that can not only increase in the presence of liver disease.
Features of the circulation of newborns
The fact is that the blood circulation of the fetus in the womb is significantly different from what is observed in already born children. During pregnancy, the baby is immersed in a bladder with amniotic fluid, and therefore his lungs are not yet familiar with air and are in a wrinkled state, that is, inoperative. But after all, a child needs a constant supply of oxygen to his tissues for their formation, growth and differentiation. That is why his blood is so closely connected with the mother's. In more detail, the baby's red blood cells simply take away oxygen from the woman's red blood cells, and for this they need a stronger ability to capture it. Therefore, his hemoglobin is represented by the F-type, which means fetal. It easily receives oxygen and carries it to the cells of the fetus.
It is also known as unconjugated bilirubin and its causes are as follows: hemolytic anemia: occurs due to premature destruction of red blood cells, inability to perform their function. Gilbert Syndrome: This is a genetic disorder in which the liver is unable to process bilirubin as a result of an enzyme deficiency. There are some basic guidelines that can help lower blood bilirubin levels: Fluid is essential to eliminate those toxins your body doesn't need.
Liver tonics such as dandelion, artichoke, verbena, or wild yam can help cleanse the liver. Alcohol is one of the biggest culprits when the liver stops working or doesn't work properly, even producing what is called a fatty liver. You should always treat it in moderation and it is better to choose beer or wine. In any case, you should avoid drinking alcohol. Food also affects liver health. Eliminate those fatty foods that can harm you and choose a healthy diet.
Results
However, after birth, such his superpower turns out to be unnecessary, because since then his lungs have opened, he breathes on his own, and he himself produces oxygen. And if his hemoglobin remains the same, then he will not be able to give it to the cells. Therefore, after the first breath, an active change of this main erythrocyte protein from fetal to adult begins - type A. This causes increased hemolysis of red blood cells and the urgent production of new, correct ones from the bone marrow. Thus, jaundice is observed in the first, suprahepatic type, which stops as soon as all the old red blood cells are destroyed, and new ones fill the bloodstream.
Basically you have to remove fat from your diet. Products such as sausages, red and white meat, processed food products and fats, fried foods, dairy products and eggs are prohibited. If bilirubin is accompanied by inflammation precisely because of the appearance of fat in the liver, salmon oil and artichoke can help you positively. In any case, remember that you should always know what high bilirubin is increased, know its causes and look for the best treatment for him. Bilirubin is a by-product of the normal breakdown of hemoglobin, when old red blood cells break down, the hemoglobin inside them becomes bilirubin.
Therapy
 The most important step in the treatment of elevated bilirubin is, of course, the treatment of the underlying disease that caused such metabolic disorders, that is, antibiotics for viral hepatitis, detoxification for poisoning, blood and red blood cell transfusion for hemolysis or severe cirrhosis. However, this should be supported by physiotherapy, hepatoprotectors, a correct lifestyle without risk factors and a special diet for elevated bilirubin. To do this, firstly, it is necessary to give up smoking and alcohol, excess fat, cholesterol, spicy and fried foods. It is strictly forbidden to use pickles and pickled foods. You should limit the consumption of salt and tea, and coffee should not be drunk at all. On the contrary, a diet with elevated bilirubin includes frequent fractional meals with an increase in the amount of lean cereals, compotes, and replacing white bread with gray bread. Indeed, thanks to the medicines prescribed by the doctor, positive dynamics will begin and, eventually, the disease will leave you.
The most important step in the treatment of elevated bilirubin is, of course, the treatment of the underlying disease that caused such metabolic disorders, that is, antibiotics for viral hepatitis, detoxification for poisoning, blood and red blood cell transfusion for hemolysis or severe cirrhosis. However, this should be supported by physiotherapy, hepatoprotectors, a correct lifestyle without risk factors and a special diet for elevated bilirubin. To do this, firstly, it is necessary to give up smoking and alcohol, excess fat, cholesterol, spicy and fried foods. It is strictly forbidden to use pickles and pickled foods. You should limit the consumption of salt and tea, and coffee should not be drunk at all. On the contrary, a diet with elevated bilirubin includes frequent fractional meals with an increase in the amount of lean cereals, compotes, and replacing white bread with gray bread. Indeed, thanks to the medicines prescribed by the doctor, positive dynamics will begin and, eventually, the disease will leave you.
Bilirubin is one of the most important components of blood, its bile pigment. If the content norm is exceeded, this is a signal of pathological changes occurring in the human body and diseases that have arisen. If bilirubin is elevated, the reasons may be different, there are many of them. The article is devoted to the reasons for the increase in the substance in the blood, the signs of an increased value, in what range the high rate is calculated in adults, and what measures should be taken to normalize the condition.
Bilirubin: origin, features, meaning
The red-brown pigment of hemoglobin catabolism is found in the human body in bile and blood. Refers to hemoglobinogenic pigments. Per normal performance substances responds to the liver.
The process of formation of bilirubin is as follows: hemoglobin contained in red blood cells supplies oxygen to tissues. Old or damaged red blood cells can be destroyed in the bone marrow, spleen or liver (during the day - about 1% of red blood cells).
Pure bilirubin is a crystalline substance, classified into two types - direct and indirect. The place of direct formation is the liver, soluble, less toxic, excreted from the body with bile. toxic, quickly penetrates into cells, quickly destroying their normal functioning. The following pigment indicators are considered normal in adults until they reach old age (about 60 years):
- General - in values from 5 to 20.5 units per 1 liter of blood mass;
- Direct - from 0 (1.7) to 5.1 units;
- Indirect - no higher than 16.5 units.
The content of the substance in men and women is almost the same.
With age human body, experiencing various overloads and the negative impact of external and internal factors, can begin to produce this pigment in an increased amount. Bilirubin increases both in diseases and from short-term exposure to various factors.
Why did the reasons for the increase in bilirubin appear - this question can be answered only after the examination.
Elevated bilirubin in the blood is present in a person in three degrees of severity:
- Light (up to 85 units);
- Medium (up to 170 units);
- Heavy (170 units and above).
What signs and symptoms would indicate an increased value
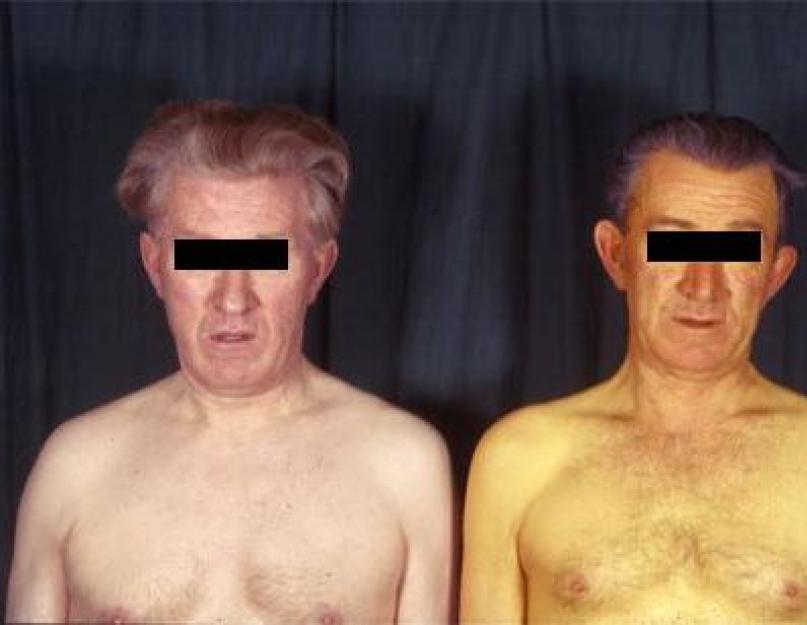
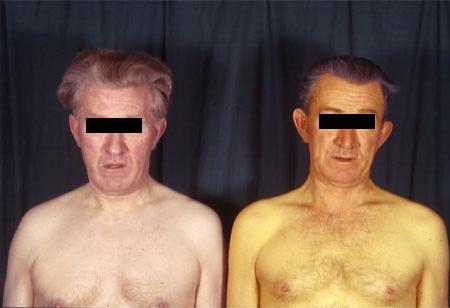
central role in metabolic processes substances allocated to the liver, most characteristic manifestation high bilirubin is jaundice and all the accompanying features: pronounced yellowing of the skin (especially clearly yellowing of the whites of the eyes), nausea, as well as attacks of dizziness and headache. However, it is important to know that an increase in bilirubin in the blood with concomitant yellowing of the skin may not be caused by its high content, but by eating large amounts of carotene-containing foods and hypothyroidism (decreased thyroid function). In this case, the sclera of the eyes will not be subject to yellowing.
What causes an increase in bilirubin levels
A normal indicator of bilirubin content can increase for three reasons, these are:
- A problem with the processing of a substance and its subsequent withdrawal (observed in liver diseases; as a result of successive processes, an unprocessed substance enters the body).
- Accelerated process of breakdown of red blood cells (especially inherent in anemia).
- Abnormal changes in the outflow of bile.
Increase in total bilirubin
Total bilirubin in adults can be exceeded for a variety of reasons:
Why direct bilirubin rises
This type of bilirubin may increase due to a violation of the outflow of bile.
The normal process is disturbed by the formation of stones in the biliary tract, pancreatitis, oncological diseases of the gallbladder or pancreas, aneurysm of the liver artery - here bilirubin is elevated for reasons characteristic of the listed disease states.
Compression of the bile ducts due to the presence of a tumor process in the gallbladder, an increase lymph nodes, as well as inflammatory processes in the excretory tract, which soon leads to a narrowing of the lumen and the formation of sclerosis of the biliary tract - the causes of increased bilirubin.
For a high rate in oncology of the gallbladder or pancreas, as well as the presence of stones in the gallbladder, signs of elevated bilirubin are characteristic:
- Bright icteric coloration of the skin;
- Strong pruritus with numerous combs;
- Violation of the natural color of the discharge ( stool become white, urine - dark);
- Various disorders of the gastrointestinal intestinal tract(diarrhea, constipation, flatulence);
- Nausea, severe belching, decreased appetite.
This pathology can lead to several types of hepatitis (viral, chronic, autoimmune, toxic, bacterial, drug), as well as oncological diseases of the liver, pancreas and gallbladder.
In all these cases, the bile stream does not enter the stomach, but is concentrated in the blood.
As evidenced by the high rate of indirect view
The main explanation for indirect high bilirubin is the destruction of red blood cells in excess amounts. Similar pathology have:
- Hemolytic anemia of several types
- Toxic (formed when poisoned by poisons, mushrooms, heavy metals);
- Medicinal (occurs as a result of taking aspirin, penicillin, insulin, levomethycin);
- Diseases that have an infectious basis;
- Named diseases - Lucy-Driscoll syndromes (a rare case of inheritance of non-hemalitic jaundice), Gilbert (lack of liver enzymes, inherited) and Crigler-Najjar (malignant liver disease, which has a hereditary basis).
Of the listed names, Gilbert's syndrome is diagnosed more often than others, which has a hereditary character, in which hyperbilirubinemia proceeds benignly, from which the prognosis is favorable.
The syndrome is named after a French doctor who identified a gene defect in the second chromosome that causes the disease.
As a rule, a sick person does not need special treatment.
How and what is treated
To make a decision on the methods of treatment, it is necessary to find out the reasons for the high value of bilirubin and coordinate the technique with a specialist, since only a doctor can identify and assess the degree of the pathology that has arisen.
Assigned tests to determine viral hepatitis, liver samples, ultrasound of the liver, as well as other necessary studies.
The main way to reduce the high rate of the substance is infusion therapy. The method is as follows: various concentrated solutions of a certain volume are introduced into the bloodstream to correct or prevent the observed losses of the body. This therapy is used in the most "severe" cases.
The method of phototherapy has proven itself well, when the patient is irradiated with special lamps. From ultraviolet rays, indirect toxic bilirubin is first destroyed, then converted to a direct form, and finally leaves the body.
Newborns can be especially successfully treated by this method if they are diagnosed with an increased content of the substance and there is a need to quickly reduce it.
If it is established that bilirubin in the blood is elevated due to a malfunction in the outflow of bile, drug treatment drugs that can bring the substance to a normal state.
Quite often, the amount of a substance can be reduced by adjusting the diet, while it is necessary to categorically exclude the consumption of foods that burden the liver, especially carbonated drinks, as well as spicy and fried foods.
Favorably affect the use of lean meat, soups on dairy or vegetable broth, cottage cheese and milk. From fruits, preference should be given to bananas; in drinks, the consumption of infusions and herbal teas will be the best choice. Such a correct, well-balanced treatment menu will help bilirubin stop rising.
When hepatitis is detected, high bilirubin is treated with liver-protecting drugs.
A high level of bilirubin in the blood is an alarming factor.
It is necessary to be aware that the diagnosed elevated bilirubin for the reasons mentioned above, as well as a number of concomitant diseases, needs proper treatment in a medical facility. In addition, the treatment promotes elimination from the body harmful products, significantly renewing body tissues. Improper or delayed treatment can lead to serious complications, any raising factor should be noticed and eliminated.