We have long been accustomed to the fact that we live in the era of space exploration. However, watching huge reusable rockets and space orbital stations today, many do not realize that the first launch of a spacecraft took place not so long ago - only 60 years ago.
Who launched the first artificial earth satellite? - THE USSR. This question is of great importance, since this event gave rise to the so-called space race between the two superpowers: the USA and the USSR.

What was the name of the world's first artificial earth satellite? - since such devices did not previously exist, Soviet scientists considered that the name "Sputnik-1" is quite suitable for this device. The code designation of the device is PS-1, which stands for "The Simplest Sputnik-1".
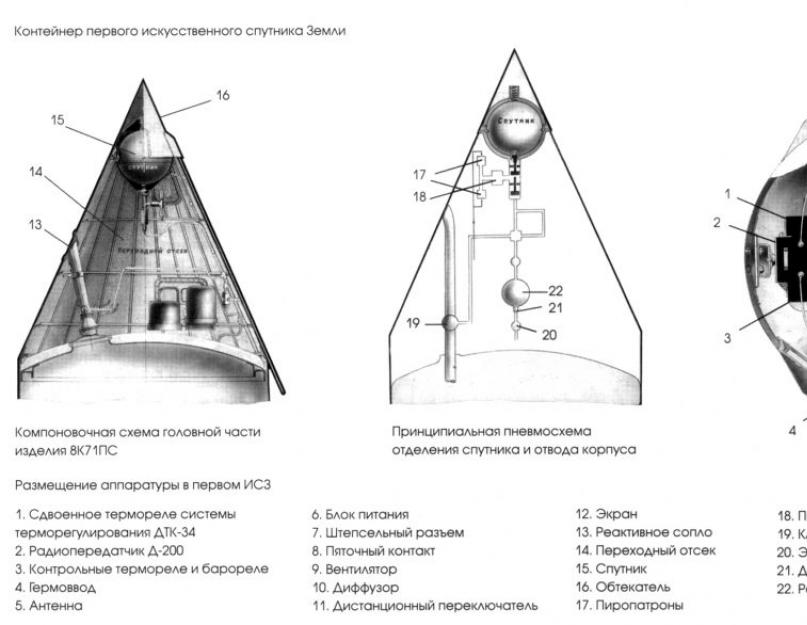
Externally, the satellite had a rather uncomplicated appearance and was an aluminum sphere with a diameter of 58 cm to which two curved antennas were attached crosswise, allowing the device to spread radio emission evenly and in all directions. Inside the sphere, made of two hemispheres fastened with 36 bolts, there were 50-kilogram silver-zinc batteries, a radio transmitter, a fan, a thermostat, pressure and temperature sensors. The total weight of the device was 83.6 kg. It is noteworthy that the radio transmitter broadcast in the range of 20 MHz and 40 MHz, that is, ordinary radio amateurs could follow it.
History of creation

The history of the first space satellite and space flights as a whole begins with the first ballistic missile - V-2 (Vergeltungswaffe-2). The rocket was developed by the famous German designer Wernher von Braun at the end of World War II. The first test launch took place in 1942, and the combat one in 1944, a total of 3225 launches were made, mainly in the UK. After the war, Wernher von Braun surrendered to the US Army, in connection with which he headed the Arms Design and Development Service in the United States. As early as 1946, a German scientist presented to the US Department of Defense a report “Preliminary design of an experimental spacecraft orbiting the Earth”, where he noted that a rocket capable of launching such a ship into orbit could be developed within five years. However, funding for the project was not approved.
On May 13, 1946, Joseph Stalin adopted a resolution on the creation of a rocket industry in the USSR. Sergei Korolev was appointed chief designer of ballistic missiles. For the next 10 years, scientists developed intercontinental ballistic missiles R-1, R2, R-3, etc.
In 1948, rocket designer Mikhail Tikhonravov gave a report to the scientific community on composite rockets and the results of calculations, according to which the developed 1000-kilometer rockets can reach great distances and even put an artificial Earth satellite into orbit. However, such a statement was criticized and was not taken seriously. Tikhonravov's department at NII-4 was disbanded due to irrelevant work, but later, through the efforts of Mikhail Klavdievich, it was reassembled in 1950. Then Mikhail Tikhonravov spoke directly about the mission to put a satellite into orbit.
satellite model
After the creation of the R-3 ballistic missile, its capabilities were presented at the presentation, according to which the missile was capable of not only hitting targets at a distance of 3000 km, but also launching a satellite into orbit. So by 1953, scientists still managed to convince top management that the launch of an orbiting satellite was possible. And the leaders of the armed forces had an understanding of the prospects for the development and launch of an artificial Earth satellite (AES). For this reason, in 1954, a decision was made to create a separate group at NII-4 with Mikhail Klavdievich, which would be engaged in satellite design and mission planning. In the same year, Tikhonravov's group presented a space exploration program, from the launch of an artificial satellite to landing on the moon.
In 1955, a delegation of the Politburo headed by N. S. Khrushchev visited the Leningrad Metal Plant, where the construction of the two-stage rocket R-7 was completed. The impression of the delegation resulted in the signing of a decree on the creation and launch of a satellite into earth orbit in the next two years. The design of the artificial satellite began in November 1956, and in September 1957 the Simplest Sputnik-1 was successfully tested on a vibration stand and in a heat chamber.
Definitely to the question "who invented Sputnik-1?" — cannot be answered. The development of the first satellite of the Earth took place under the leadership of Mikhail Tikhonravov, and the creation of the launch vehicle and the launch of the satellite into orbit - under the leadership of Sergei Korolev. However, a considerable number of scientists and researchers worked on both projects.
Launch history

In February 1955, the top management approved the creation of the Scientific Research Test Site No. 5 (later Baikonur), which was to be located in the Kazakhstan desert. The first ballistic missiles of the R-7 type were tested at the test site, but according to the results of five experimental launches, it became clear that the massive warhead of the ballistic missile could not withstand the temperature load and needed to be improved, which would take about six months. For this reason, S.P. Korolev requested two rockets from N.S. Khrushchev for the experimental launch of PS-1. At the end of September 1957, the R-7 rocket arrived at Baikonur with a lightened head and a passage under the satellite. Extra equipment was removed, as a result of which the mass of the rocket was reduced by 7 tons.
On October 2, S.P. Korolev signed the order on flight tests of the satellite and sent a notice of readiness to Moscow. And although no answers came from Moscow, Sergei Korolev decided to bring the Sputnik launch vehicle (R-7) from PS-1 to the starting position.
The reason why the management demanded that the satellite be put into orbit during this period is that from July 1, 1957 to December 31, 1958, the so-called International Geophysical Year was held. According to it, during the specified period, 67 countries jointly and under a single program carried out geophysical research and observations.
The launch date of the first artificial satellite is October 4, 1957. In addition, on the same day, the opening of the VIII International Astronautical Congress took place in Spain, Barcelona. The leaders of the USSR space program were not disclosed to the public due to the secrecy of the work being carried out; Academician Leonid Ivanovich Sedov informed Congress about the sensational launch of the satellite. Therefore, it was the Soviet physicist and mathematician Sedov that the world community has long considered the "father of Sputnik."
Flight history

At 22:28:34 Moscow time, a rocket with a satellite was launched from the first site of NIIP No. 5 (Baikonur). After 295 seconds, the central block of the rocket and the satellite were launched into an elliptical Earth orbit (apogee - 947 km, perigee - 288 km). After another 20 seconds, PS-1 separated from the missile and gave a signal. It was the repeated signals of “Beep! Beep!”, which were caught at the range for 2 minutes, until Sputnik-1 disappeared over the horizon. On the first orbit of the apparatus around the Earth, the Telegraph Agency of the Soviet Union (TASS) transmitted a message about the successful launch of the world's first satellite.
After receiving the PS-1 signals, detailed data began to come in about the device, which, as it turned out, was close to not reaching the first space velocity and not entering orbit. The reason for this was an unexpected failure of the fuel control system, due to which one of the engines was late. A fraction of a second separated from failure.
However, PS-1 nevertheless successfully reached an elliptical orbit, along which it moved for 92 days, while completing 1440 revolutions around the planet. The radio transmitters of the device worked during the first two weeks. What caused the death of the first satellite of the Earth? - Having lost speed due to the friction of the atmosphere, Sputnik-1 began to descend and completely burned out in the dense layers of the atmosphere. It is noteworthy that many could observe some kind of brilliant object moving across the sky at that time. But without special optics, the shiny body of the satellite could not be seen, and in fact this object was the second stage of the rocket, which also rotated in orbit, along with the satellite.
The meaning of flight

The first launch of an artificial Earth satellite in the USSR produced an unprecedented rise in pride for their country and swipe by US prestige. An excerpt from the United Press publication: “90 percent of the talk about artificial Earth satellites came from the United States. As it turned out, 100 percent of the case fell on Russia ... ". And despite the erroneous ideas about the technical backwardness of the USSR, it was the Soviet apparatus that became the first satellite of the Earth, moreover, its signal could be tracked by any radio amateur. The flight of the first Earth satellite marked the beginning of the space age and launched the space race between the Soviet Union and the United States.
Just 4 months later, on February 1, 1958, the United States launched its Explorer 1 satellite, which was assembled by the team of scientist Wernher von Braun. And although it was several times lighter than the PS-1 and contained 4.5 kg of scientific equipment, it was still the second one and no longer had such an impact on the public.
Scientific results of PS-1 flight
The launch of this PS-1 had several goals:
- Testing the technical ability of the apparatus, as well as checking the calculations made for the successful launch of the satellite;
- Research of the ionosphere. Before the launch of the spacecraft, radio waves sent from the Earth were reflected from the ionosphere, excluding the possibility of studying it. Now, scientists have been able to begin exploring the ionosphere through the interaction of radio waves emitted by a satellite from space and traveling through the atmosphere to the Earth's surface.
- Calculation of the density of the upper layers of the atmosphere by observing the rate of deceleration of the apparatus due to friction against the atmosphere;
- Investigation of the influence of outer space on equipment, as well as determining favorable conditions for the operation of equipment in space.
Listen to the sound of the First Satellite
And although the satellite did not have any scientific equipment, tracking its radio signal and analyzing its nature yielded many useful results. So a group of scientists from Sweden measured the electronic composition of the ionosphere, based on the Faraday effect, which says that the polarization of light changes when it passes through a magnetic field. Also, a group of Soviet scientists from Moscow State University developed a method for observing the satellite with an accurate determination of its coordinates. Observation of this elliptical orbit and the nature of its behavior made it possible to determine the density of the atmosphere in the region of orbital heights. The unexpectedly increased density of the atmosphere in these areas prompted scientists to create a theory of satellite deceleration, which contributed to the development of astronautics.

Video about the first satellite.
In 1957, under the leadership of S.P. Korolev, the world's first intercontinental ballistic missile R-7 was created, which in the same year was used to launch the world's first artificial earth satellite.
artificial earth satellite (satellite) is a spacecraft revolving around the Earth in a geocentric orbit. - the trajectory of the movement of a celestial body along an elliptical trajectory around the Earth. One of the two foci of the ellipse along which the celestial body moves coincides with the Earth. In order to spaceship found himself in this orbit, he needs to be informed of a speed that is less than the second cosmic velocity, but not less than the first cosmic velocity. AES flights are carried out at altitudes up to several hundred thousand kilometers. The lower limit of the satellite flight altitude is determined by the need to avoid the process of rapid deceleration in the atmosphere. The orbital period of a satellite, depending on the average flight altitude, can range from one and a half hours to several days.

Of particular importance are satellites in geostationary orbit, the period of revolution of which is strictly equal to a day, and therefore, for a ground observer, they “hang” motionlessly in the sky, which makes it possible to get rid of rotary devices in antennas. geostationary orbit(GSO) - a circular orbit located above the Earth's equator (0 ° latitude), in which an artificial satellite revolves around the planet with an angular velocity equal to the angular velocity of the Earth's rotation around its axis. Movement of an artificial Earth satellite in geostationary orbit.
Sputnik-1- the first artificial satellite of the Earth, the first spacecraft, launched into orbit in the USSR on October 4, 1957.
Satellite code - PS-1(The simplest Sputnik-1). The launch was carried out from the 5th Tyura-Tam research site of the USSR Ministry of Defense (later this place was called the Baikonur Cosmodrome) on a Sputnik launch vehicle (R-7).
Scientists M. V. Keldysh, M. K. Tikhonravov, N. S. Lidorenko, V. I. Lapko, B. S. Chekunov, A. V. Bukhtiyarov and many others.
The date of the launch of the first artificial satellite of the Earth is considered the beginning of the space age of mankind, and in Russia it is celebrated as a memorable day for the Space Forces.

The body of the satellite consisted of two hemispheres with a diameter of 58 cm made of aluminum alloy with docking frames interconnected by 36 bolts. The tightness of the joint was provided by a rubber gasket. Two antennas were located in the upper half-shell, each of two pins 2.4 m and 2.9 m each. Since the satellite was not oriented, the four-antenna system gave uniform radiation in all directions.
A block of electrochemical sources was placed inside the hermetic case; radio transmitting device; fan; thermal relay and air duct of the thermal control system; switching device of onboard electroautomatics; temperature and pressure sensors; onboard cable network. Mass of the first satellite: 83.6 kg.
The history of the creation of the first satellite
On May 13, 1946, Stalin signed a decree on the creation in the USSR of the rocket branch of science and industry. In August S. P. Korolev was appointed chief designer of long-range ballistic missiles.

But back in 1931, the Jet Propulsion Study Group was created in the USSR, which was engaged in the design of rockets. This group worked Zander, Tikhonravov, Pobedonostsev, Korolev. In 1933, on the basis of this group, the Jet Institute was organized, which continued work on the creation and improvement of rockets.
In 1947, the V-2 rockets were assembled and tested in Germany, and they marked the beginning of Soviet work on the development of rocket technology. However, the V-2 embodied in its design the ideas of lone geniuses Konstantin Tsiolkovsky, Hermann Oberth, Robert Goddard.
In 1948, the R-1 rocket, which was a copy of the V-2, manufactured entirely in the USSR, was already being tested at the Kapustin Yar test site. Then the R-2 appeared with a flight range of up to 600 km, these missiles were put into service since 1951. And the creation of the R-5 missile with a range of up to 1200 km was the first separation from the V-2 technology. These missiles were tested in 1953, and immediately began research into their use as a carrier of nuclear weapons. On May 20, 1954, the government issued a decree on the development of a two-stage intercontinental rocket R-7. And already on May 27, Korolev sent a memorandum to the Minister of Defense Industry D.F. Ustinov on the development of artificial satellites and the possibility of launching it using the future R-7 rocket.
Launch!
On Friday, October 4, at 22 hours 28 minutes 34 seconds Moscow time, successful launch. 295 seconds after the launch, PS-1 and the central block of the rocket weighing 7.5 tons were launched into an elliptical orbit with an altitude of 947 km at apogee and 288 km at perigee. At 314.5 seconds after the launch, Sputnik separated and he gave his vote. "Beep! Beep! - so sounded his call signs. They were caught at the training ground for 2 minutes, then the Sputnik went beyond the horizon. People at the cosmodrome ran out into the street, shouting "Hurrah!", rocked the designers and the military. And even on the first orbit, a TASS message sounded: "... As a result of the great hard work of research institutes and design bureaus, the world's first artificial satellite of the Earth was created ..."
Only after receiving the first signals of the Sputnik did the results of telemetry data processing arrive and it turned out that only a fraction of a second separated from failure. One of the engines was “late”, and the time to enter the regime is tightly controlled and if it is exceeded, the start is automatically canceled. The block went into mode less than a second before the control time. At the 16th second of the flight, the fuel supply control system failed, and due to the increased consumption of kerosene, the central engine turned off 1 second ahead of the estimated time. But the winners are not judged! The satellite flew for 92 days, until January 4, 1958, making 1440 revolutions around the Earth (about 60 million km), and its radio transmitters worked for two weeks after launch. Due to friction against the upper layers of the atmosphere, the satellite lost speed, entered the dense layers of the atmosphere and burned out due to friction against the air.
Officially "Sputnik-1" and "Sputnik-2", Soviet Union launched in accordance with the obligations assumed for the International Geophysical Year. The satellite emitted radio waves at two frequencies of 20.005 and 40.002 MHz in the form of telegraph packets with a duration of 0.3 s, this made it possible to study the upper layers of the ionosphere - before the launch of the first satellite, it was possible to observe only the reflection of radio waves from the regions of the ionosphere lying below the zone of maximum ionization of the ionospheric layers.

Launch goals
- verification of calculations and main technical solutions adopted for the launch;
- ionospheric studies of the passage of radio waves emitted by satellite transmitters;
- experimental determination of the density of the upper atmosphere by satellite deceleration;
- study of the operating conditions of the equipment.
Despite the fact that there was no scientific equipment on the satellite, the study of the nature of the radio signal and optical observations beyond orbit provided important scientific data.
Other satellites
The second country to launch a satellite was the United States: on February 1, 1958, an artificial earth satellite was launched Explorer-1. It was in orbit until March 1970, but stopped broadcasting as early as February 28, 1958. The first American artificial earth satellite was launched by Brown's team.

Werner Magnus Maximilian von Braun- German, and since the late 1940s, an American designer of rocket and space technology, one of the founders of modern rocket science, the creator of the first ballistic missiles. In the US, he is considered the "father" of the American space program. Von Braun, for political reasons, was not given permission to launch the first American satellite for a long time (the US leadership wanted the satellite to be launched by the military), so preparations for the launch of the Explorer began in earnest only after the Avangard accident. For launch, a boosted version of the Redstone ballistic missile, called the Jupiter-S, was created. The mass of the satellite was exactly 10 times less than the mass of the first Soviet satellite - 8.3 kg. It was equipped with a Geiger counter and a meteor particle sensor. The Explorer's orbit was noticeably higher than the orbit of the first satellite..

The following countries that launched satellites - Great Britain, Canada, Italy - launched their first satellites in 1962, 1962, 1964 . in American launch vehicles. And the third country that launched the first satellite on its launch vehicle was France November 26, 1965
Now satellites are being launched more than 40 countries (as well as individual companies) with the help of both their own launch vehicles (LV) and those provided as launch services by other countries and interstate and private organizations.

October 4 marks the Day of the beginning of the space age of mankind, proclaimed by the International Federation of Astronautics in September 1967. On this day, October 4, 1957, the world's first artificial Earth satellite was launched in the USSR.
Scientists Mstislav Keldysh, Mikhail Tikhonravov, Nikolai Lidorenko, Vladimir Lapko, Boris Chekunov and many others worked on its creation, headed by the founder of practical astronautics Sergei Korolev.
Being engaged in the creation of long-range ballistic missiles and especially the R-7 intercontinental missile, Sergei Korolev constantly returned to the idea of practical space exploration. On May 27, 1954, he turned to the Minister of Defense Industry of the USSR Dmitry Ustinov with a proposal to develop an artificial Earth satellite (AES). In June 1955, a memorandum was prepared on the organization of work on space objects, and in August of the same year, data on the parameters of a spacecraft for a flight to the Moon.
The resolution on work on satellites was adopted on January 30, 1956. It was originally intended to be more complex and heavy.
However, the work was delayed, and it was decided to develop the simplest apparatus, so as not to give way to the United States involved in a similar project.
In January 1957, Korolev sent a memorandum to the Council of Ministers of the USSR. In it, he said that in April-June 1957 two missiles in the satellite version could be prepared "and launched immediately after the first successful launches of an intercontinental missile." The first Soviet intercontinental ballistic missile successfully launched on August 21, 1957.
The satellite, which became the first artificial celestial body, was launched into orbit on October 4, 1957 by an R-7 launch vehicle from the 5th Research Test Site of the USSR Ministry of Defense, which later received the open name Baikonur Cosmodrome.
The launched spacecraft PS-1 (the simplest satellite-1) was a ball with a diameter of 58 centimeters, weighed 83.6 kilograms, was equipped with four pin antennas 2.4 and 2.9 meters long for transmitting signals from battery-powered transmitters. 295 seconds after the launch, the PS-1 and the central block of the rocket weighing 7.5 tons were launched into an elliptical orbit with an altitude of 947 kilometers at apogee and 288 kilometers at perigee. At 315 seconds after the launch, the artificial Earth satellite separated from the second stage of the launch vehicle, and the whole world immediately heard its call signs.
The material was prepared on the basis of information from open sources
The first artificial Earth satellite was created and launched into space in the USSR. It happened on October 4, 1957. On this day, radio stations around the world interrupted their transmissions to announce the most important news. The Russian word "satellite" has entered into all languages of the world.
It was a fantastic breakthrough of mankind in the exploration of outer space, and it laid the foundation for the great Space Age of all mankind. And the palm rightfully belongs to the USSR.
Here is a picture taken in the lobby of the Space Research Institute Russian Academy Sciences.

In the foreground is the First Sputnik, the highest technological achievement of its time.
On the second - employees of IKI - outstanding scientists, creators of the first satellite, atomic weapons, space science and technology.
If it is not readable in the picture, here are their names:
- Yakov Borisovich Zeldovich - theoretical physicist, repeatedly awarded the Stalin Prize of the 1st degree for special work related to the atomic bomb. Three times Hero of Socialist Labor.
October 4, 1957 forever entered the history of mankind as the beginning of a new era - space. It was on this day that the first artificial satellite (AES) - Sputnik-1 - was sent to surf space from the Baikonur Cosmodrome. It weighed relatively little - 83.6 kilograms, but at that time delivering even such a "crumb" into orbit was a very serious task.
I think that in Russia there is no person who would not know who was the first man in space.
With the first satellite, the situation is more complicated. Many do not even know what country he belonged to.
Thus began a new era in science and the legendary space race between the USSR and the USA.
The era of rocket science begins at the beginning of the last century, with theory. It was then that the outstanding scientist Tsiolkovsky, in his article on the jet engine, actually predicted the appearance of satellites. Despite the fact that the professor had many students who continued to popularize his ideas, many considered him to be just a dreamer.
Then new times came, the country had a lot of things to do and problems, except for rocket science. But two decades later, Friedrich Zander and the now famous aviator engineer Korolenko founded a group to study jet propulsion. After that, there were several events that led to the fact that 30 years later the first satellite was launched into space, and after some time, a man:
- 1933 - launch of the first rocket with a jet engine;
- 1943 - the invention of the German V-2 rockets;
- 1947–1954 - rocket launches P1-P7.
The apparatus itself was ready in mid-May at 7 pm. His device was quite simple, there were 2 beacons on it, which made it possible to measure the trajectory of his flight. Interestingly, after sending a notice that the satellite was ready for flight, Korolev did not receive any answer from Moscow and independently decided to place the satellite on the starting position.

The preparation and launch of the satellite was led by S.P. Korolev. The satellite made 1440 complete revolutions in 92 days, after which it burned down, entering the dense layers of the atmosphere. The radio transmitters worked for two weeks after the launch.
The first satellite was given the name PS-1. When the project of the first-born space was born, there were disputes among engineers and developers: what should it be in shape? After listening to the arguments of all parties, Sergei Pavlovich categorically stated: "A ball and only a ball!" - and, without waiting for questions, he explained his plan: “The ball, its shape, the conditions of its habitat from the point of view of aerodynamics have been thoroughly studied.
Known for its pros and cons. And this is of no small importance.
Understand - FIRST! When humanity sees an artificial satellite, it should evoke good feelings in it. What could be more expressive than a ball? It is close to the shape of our natural celestial bodies solar system. People will perceive the satellite as a kind of image, as a symbol of the space age!
I consider it necessary to install such transmitters on board so that radio amateurs on all continents can receive their call signs. The orbital flight of the satellite is calculated in such a way that, using the simplest optical instruments, everyone from the Earth can see the flight of the Soviet satellite.
On the morning of October 3, 1957, scientists, designers, members of the State Commission gathered at the assembly and test building - everyone who was associated with the launch. They were waiting for the two-stage rocket and space system Sputnik to be taken to the launch pad.
The metal gates opened. The locomotive, as it were, pushed out a rocket placed on a special platform. Sergei Pavlovich, setting up a new tradition, took off his hat. His example of high respect for the work that created this miracle of technology was followed by others.
Korolev took a few steps behind the rocket, stopped and, according to the old Russian custom, said: “Well, with God!”.
Before the start of the space age, there were only a few hours left. What awaited Korolev and his associates? Will October 4 be the victorious day that he dreamed of for many years? The sky, studded with stars that night, seemed to become closer to the Earth. And everyone who was present at the launch pad involuntarily looked at Korolev. What was he thinking about as he looked into the dark sky, twinkling with myriads of near and far stars? Perhaps he remembered the words of Konstantin Eduardovich Tsiolkovsky: “The first great step of mankind is to fly out of the atmosphere and become a satellite of the Earth”?
The last meeting of the State Commission before the start. There was a little more than an hour left before the start of the experiment. The floor was given to S.P. Korolev, everyone was waiting for a detailed report, but the chief designer was brief: “The launch vehicle and satellite passed the launch tests. I propose to launch the rocket and space complex at the appointed time, today at 22:28.”
And here is the long-awaited launch!
"THE FIRST ARTIFICIAL EARTH SATELLITE, A SOVIET SPACE VEHICLE LAUNCHED INTO ORBIT."
The launch was carried out from the 5th Tyura-Tam research site of the USSR Ministry of Defense on a Sputnik launch vehicle, created on the basis of the R7 intercontinental ballistic missile.
On Friday, October 4, at 22:28:34 Moscow time (19:28:34 GMT), a successful launch was made.
295 seconds after the launch of the PS-1 and the central block (stage II) of the rocket weighing 7.5 tons were launched
elliptical orbit with a height of 947 km at apogee and 288 km at perigee. The apogee was in the Southern Hemisphere and the perigee was in the Northern Hemisphere. 314.5 seconds after the launch, the protective cone was dropped and Sputnik separated from the second stage of the launch vehicle, and he gave his vote. "Beep! Beep! - so sounded his call signs.
They were caught at the training ground for 2 minutes, then the Sputnik went beyond the horizon. People at the cosmodrome ran out into the street, shouting "Hurrah!", rocked the designers and the military.
And on the first orbit, a TASS message sounded:
"As a result of the great hard work of research institutes and design bureaus, the world's first artificial Earth satellite has been created."
Only after receiving the first signals of the Sputnik did the results of telemetry data processing arrive and it turned out that only a fraction of a second separated from failure. Before the start, the engine in the G block was “delayed”, and the time to enter the regime is tightly controlled, and if it is exceeded, the start is automatically canceled.
The block went into mode less than a second before the control time. At the 16th second of the flight, the tank emptying system (SES) failed, and due to the increased consumption of kerosene, the central engine turned off 1 second ahead of the estimated time. According to the memoirs of B. E. Chertok: “A little more - and the first cosmic speed could not be achieved.
But the winners are not judged! Great things have happened!"
The orbital inclination of Sputnik-1 was about 65 degrees, which meant that Sputnik-1 flew approximately between the Arctic Circle and the Antarctic Circle, due to the rotation of the Earth during each revolution, shifting by 24 degrees in longitude 37.
The orbital period of Sputnik-1 was initially 96.2 minutes, then it gradually decreased due to the decrease in orbit, for example, after 22 days it became 53 seconds shorter.
History of creation
The flight of the first satellite was preceded by a long work of scientists and designers, in which scientists played a significant role.
Here are their names:
- Valentin Semenovich Etkin - sounding of the Earth's surface from space by remote radiophysical methods.
- Pavel Efimovich Elyasberg - during the launch of the first Artificial Earth Satellite, he supervised the work on determining the orbits and predicting the satellite's motion based on the results of measurements.
- Yan Lvovich Ziman - Ph.D. thesis, defended at MIIGAiK, was devoted to the selection of orbits for satellites.
- Georgy Ivanovich Petrov - together with S.P. Korolev and M.V. Keldysh, who stood at the origins of astronautics.
- Iosif Samuilovich Shklovsky - founder of the school of modern astrophysics.
- Georgiy Stepanovich Narimanov - programs and methods of navigation and ballistic support in controlling the flights of artificial earth satellites.
- Konstantin Iosifovich Gringauz, the first artificial Earth satellite, launched in 1957, carried on board a radio transmitter created by a scientific and technical group led by K. I. Gringauz.
- Yuri Ilyich Galperin - magnetospheric research.
- Semyon Samoilovich Moiseev - plasma and hydrodynamics.
- Vasily Ivanovich Moroz - Physics of planets and small bodies of the solar system.
satellite device
The satellite body consisted of two power hemispherical shells with a diameter of 58.0 cm made of aluminum-magnesium alloy AMg-6 2 mm thick with docking frames interconnected by 36 M8 × 2.5 studs. Before launch, the satellite was filled with dry nitrogen gas at a pressure of 1.3 atmospheres. The tightness of the joint was ensured by a gasket made of vacuum rubber. The upper half-shell had a smaller radius and was covered with a hemispherical outer screen 1 mm thick to provide thermal insulation.

The shell surfaces were polished and processed to give them special optical properties. On the upper half-shell, two corner vibrator antennas were located crosswise, facing back; each consisted of two arms-pins 2.4 m long (VHF antenna) and 2.9 m each (HF antenna), the angle between the arms in a pair was 70 °; the shoulders were bred to the required angle with a spring
mechanism after separation from the launch vehicle.
Such an antenna provided radiation close to uniform in all directions, which was required for stable radio reception due to the fact that the satellite was not oriented. The design of the antennas was proposed by G. T. Markov (MPEI). On the front half-shell there were four sockets for mounting antennas with pressure seal fittings and a filling valve flange. On the rear half-shell there was an interlocking heel contact, which included an autonomous on-board power supply after the separation of the satellite from the launch vehicle, as well as a flange of the test system connector.

Scheme of the orbit of the first satellite of the Earth. /From the newspaper "Soviet Aviation"/. 1957
Inside the sealed case were placed:
- block of electrochemical sources (silver-zinc accumulators);
- radio transmitting device;
- a fan that is switched on by a thermal relay at temperatures above +30°С and switched off when the temperature drops to +20…23°С;
- thermal relay and air duct of the thermal control system;
- switching device of onboard electroautomatics; temperature and pressure sensors;
- onboard cable network. Weight - 83.6 kg.

Flight parameters
- The flight began on October 4, 1957 at 19:28:34 GMT.
- The end of the flight - January 4, 1958.
- The mass of the device is 83.6 kg.
- The maximum diameter is 0.58 m.
- Orbital inclination - 65.1°.
- The circulation period is 96.2 minutes.
- Perigee - 228 km.
- Apogee - 947 km.
- Vitkov - 1440.
Memory
In honor of the beginning of the space age of mankind in 1964, a 99-meter obelisk "To the Conquerors of Space" was opened in Moscow on Mira Avenue.

In honor of the 50th anniversary of the launch of Sputnik-1, on October 4, 2007, a monument to the First Artificial Earth Satellite was unveiled in the city of Korolev on Cosmonauts Avenue.

An ice plateau on Pluto was named after Sputnik 1 in 2017.
Picking up speed, the rocket confidently went up. Everyone who was involved in the launch of the satellite gathered at the launch pad. The nervous excitement did not subside. Everyone was waiting for the satellite to circle the Earth and appear above the spaceport. “There is a signal,” the voice of the operator rang out over the speakerphone.
At the same second, the sonorous, confident voice of the companion poured out of the speaker over the steppe. Everyone applauded in unison. Someone shouted "Hurrah!", The victory cry was picked up by the rest. Strong handshakes, hugs. An atmosphere of happiness reigned ... Korolev looked around: Ryabinin, Keldysh, Glushko, Kuznetsov, Nesterenko, Bushuev, Pilyugin, Ryazansky, Tikhonravov. Everyone is here, everything is nearby - "a mighty bunch in science and technology", adherents of the ideas of Tsiolkovsky.
It seemed that the general rejoicing of those gathered at that moment on the launch pad could not be appeased. But Korolev got up on the impromptu podium. Silence reigned. He did not hide his joy: his eyes shone, his face, usually stern, shone.
“Today, what the best sons of mankind dreamed of, and among them our famous scientist Konstantin Eduardovich Tsiolkovsky, has come true. He brilliantly predicted that mankind would not remain forever on Earth. The satellite is the first confirmation of his prophecy. The space storm has begun. We can be proud that our Motherland started it. To all - a big Russian thank you!
Here are reviews from the foreign press.
The Italian scientist Beniamino Segre, learning about the satellite, said: "As a person and as a scientist, I am proud of the triumph of the human mind, emphasizing the high level of socialist science."
Review of the New York Times: “The success of the USSR first of all shows that this is the greatest feat of Soviet science and technology. Such a feat could only be accomplished by a country with first-class conditions in a very wide field of science and technology.
The statement of the German rocket scientist Herman Oberth is curious: “Only a country with a huge scientific and technical potential could successfully solve such a difficult task as launching the first satellite of the Earth. It was also necessary to have a considerable number of specialists. And the Soviet Union has them. I admire the talent of Soviet scientists.”
The most profound assessment of what happened was given by physicist, Nobel Prize winner Frederic Joliot-Curie: “This a great victory man, which is a turning point in the history of civilization. Man is no longer chained to his planet."
In all languages of the world on this day it sounded: “cosmos”, “satellite”, “USSR”, “Russian scientists”.
In 1958 S.P. Korolev makes a report "On the program of exploration of the Moon", supervises the launch of a geophysical rocket with research equipment and two dogs in the descender, participates in organizing the flight of the third artificial Earth satellite - the first scientific station. And a lot more other scientific work was done under his direction.
And finally, the triumph of science - April 12, 1961. Sergei Pavlovich Korolev - leader of the historic human space flight. This day became an event in the history of mankind: for the first time, a man defeated the earth's gravity and rushed into outer space ... Then real courage and courage were required to get into a "space ball", as the ship "Vostok" was sometimes called, and, not thinking about one's own fate, fly away into the boundless starry space.
The day before, Korolev addressed the members of the State Commission: “Dear comrades! Less than four years have passed since the launch of the first artificial Earth satellite, and we are already ready for the first manned flight into space. There is a group of cosmonauts here, each of them is ready to make a flight. It was decided that Yuri Gagarin would fly first. Others will follow him in the near future. Next in line we have new flights that will be interesting for science and for the benefit of mankind.”
Korolev's Martian project remained unfinished. New ones will come, those who will continue this project and lead their ships along the Milky Way to distant planets, to distant worlds...
On my own behalf, I can add that the glory of the Fatherland is brought and will be brought by the heroes of science, who imprinted Knowledge with their lives.
Above us are the same, as of old, heaven,
And the streams pour their blessings to us in the same way,
And miracles are happening today
And in our day there are prophets...
(V.G. Benediktov)
On October 4, 1957, the space age of humanity began. The first artificial Earth satellite was launched from the 5th Scientific Research Test Site of the USSR Ministry of Defense, which later became known as the Baikonur Cosmodrome.
The creation of the first spacecraft began at OKB-1 in November 1956. The satellite was designed as a very simple device, which is why it was called the PS-1 spacecraft (the simplest satellite). It was a ball with a diameter of 58 centimeters and a weight of 83.6 kilograms. The PS-1 was equipped with four whip antennas for transmitting signals from battery-powered transmitters.
A whole group of scientists and designers headed by the founder of practical cosmonautics Sergei Korolev worked on the creation of an artificial satellite of the Earth.
Exhibit of the Museum of the History of the Baikonur Cosmodrome
On October 4, 1957 at 22:28:34 Moscow time, the Sputnik launch vehicle (R-7) was successfully launched. 295 seconds after launch, the first satellite was launched into an elliptical orbit with an altitude of 947 km at the apogee and 288 km at the perigee. At 315 seconds after the launch, the satellite separated, and he gave his vote. "Beep! Beep! - that's what his call signs sounded like. PS-1 became the first artificial object The satellite flew for 92 days, made 1440 revolutions around the Earth (flying about 60 million km), and its battery-powered radio transmitters worked for two weeks after launch.

Newspaper "Pravda" of October 5 and 6, 1957 

In September 1967, the International Astronautical Federation proclaimed October 4 as the Day of the Beginning of the Human Space Age. Also, the date of the launch of the first artificial satellite of the Earth is considered the day of the Space Forces. It was the parts of the launch and control of spacecraft that launched and controlled the flight of the first artificial satellite of the Earth. Subsequently, the first manned flight into space and many domestic and international space programs were carried out with the direct participation of military units for launching and controlling spacecraft. In connection with the increasing role of outer space in matters of national security, by Decree of the President of Russia in 2001, an independent branch of the military was created - the Space Forces. Today, the Space Forces are part of the VKS of the Russian Armed Forces.